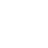
Inhibin B Detection Kit (INH-B)
Inhibin B is a glycoprotein produced predominantly by Sertoli cells which regulates pituitary FSH release by a negative feedback loop. Inhibin B is the best and most direct marker for evaluating male spermatogenesis.
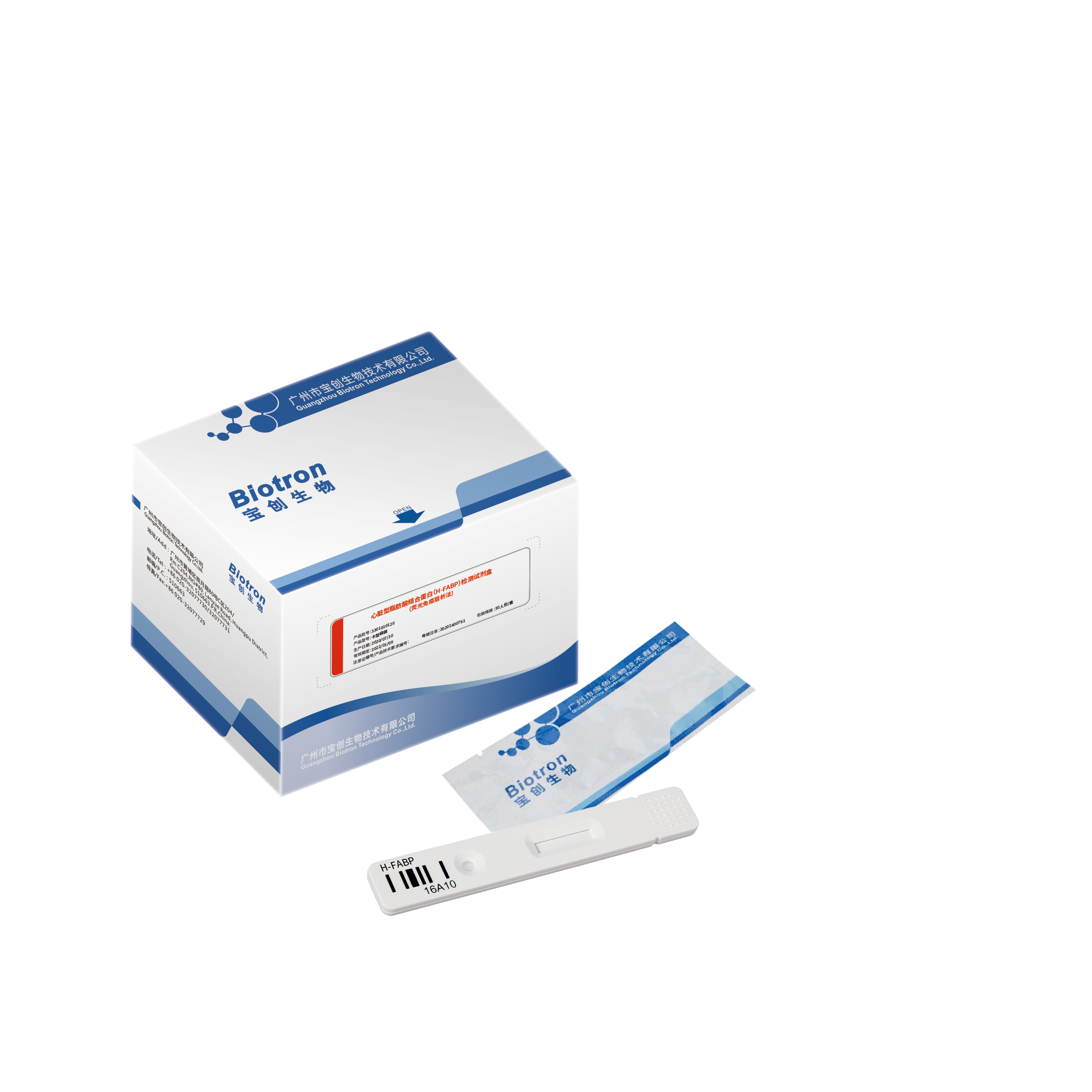
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
DESCRIPTION
Successfully obtained in the EU CE access certification
Passed ISO13485 certification
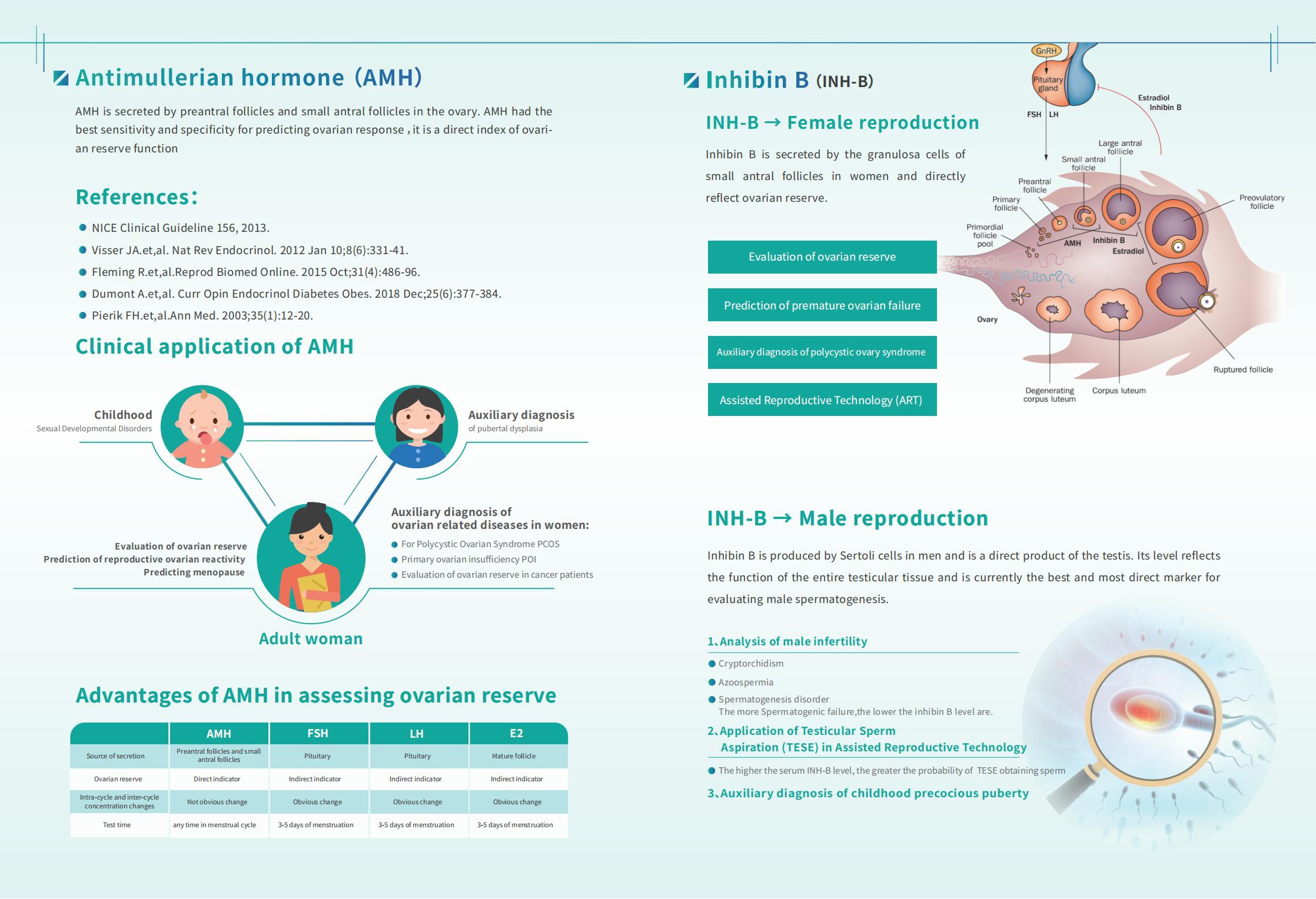
→ Female reproduction
Inhibin B is secreted by the granulosa cells of small antral follicles in women and directly reflect ovarian reserve.
→ Male reproduction
Inhibin B is produced by Sertoli cells in males, and its level reflects the function of the entire testicular tissue . Inhibin B is the best and most direct marker for evaluating male spermatogenesis.
INH-B:a novel marker of spermatogenesis
Subfertility affects about 15% of all couples. Assessment of spermatogenesis has a central role in the evaluation of the subfertile couple. Recently, the serum inhibin B level has emerged as a sensitive endocrine marker of spermatogenesis. The serum inhibin B level has been shown to be associated with classical markers of spermatogenesis, particularly testicular histology, and to be the most accurate endocrine marker of spermatogenesis. Schematic representation of the hypothala-mic-pituitary-testis axis in adulthood that is shown in Figure 1.
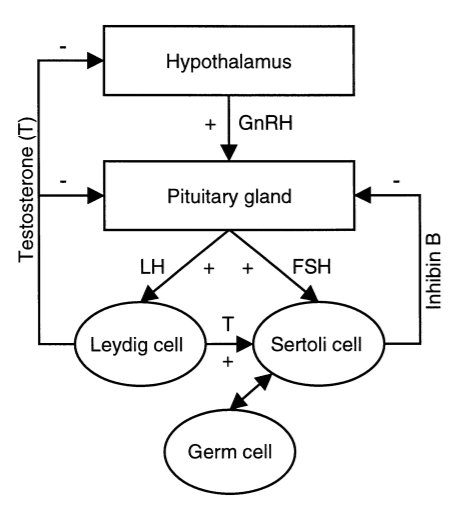
Figure 1
Schematic representation of the hypothala-mic-pituitary-testis axis in adulthood
Hypothalamic GnRH stimulates the pituitary secretion of FSH and LH. LH stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone (T). FSH and testosterone directly stimulate Sertoli cells, which in turn, regulate germ cell development. GnRH is under negative feedback control by testosterone, while pituitary secretion of LH and FSH is under feedback control by testosterone, and inhibin B causes selective inhibition of FSH production. Inhibin B is produced by Sertoli cells in interaction with specific germ cell types. GnRH = gonadotrophin-releasing hormone; FSH = follicle-stimulating hormone; LH = luteinising hormone.
Clinical significance:
• Analysis of male infertility
• Application of Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESE) in Assisted Reproductive Technology
• Auxiliary diagnosis of childhood precocious puberty
Applicable departments:
Physical examination center, reproductive center, gynecology, oncology, pediatrics
References:
1.NICE Clinical Guideline 156, 2013.
2.Visser JA.et,al. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Jan 10;8(6):331-41.
3.Fleming R.et,al.Reprod Biomed Online. 2015 Oct;31(4):486-96.
4.Dumont A.et,al. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018 Dec;25(6):377-384.
5.Pierik FH.et,al.Ann Med. 2003;35(1):12-20.
SPECIFICATION
| Sample type | Serum, plasma ,whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry, the validity period is 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box ,50 tests/box |

 Request
Request
Applicable Instrument

CATALOGS
 2 pages
2 pages