NT-proBNP Rapid Test Kit (Fluorescence immunochromatography)
The reagent is used to detect the content of N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide colloid (NT-proBNP) in human serum, plasma or whole blood samples, and is mainly used clinically for auxiliary diagnosis of heart failure.
Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
DESCRIPTION
Successfully obtained in the EU CE access certification
Passed ISO13485 certification
Heart failure (HF) biomarkers have dramatically impacted the way HF patients are evaluated and managed. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP) are the gold standard biomarkers in determining the diagnosis and prognosis of HF, and studies on natriuretic peptide-guided HF management look promising.
NT-proBNP: A gold standard for Heart Failure
International guidelines recommend the use of B-type natriuretic peptide testing in the diagnostic workup of Heart Failure (HF) in both acute and non-acute patient presentation(2).
In the emergency department (ED), NT-proBNP is particularly useful for the triage of patients with acute dyspnea and suspected acute HF. It is highly sensitive and specific for exclusion (single rule-out cut-off value of 300 pg/mL) or confirmation of acute HF (age-adjusted rule-in cut-off values) (3).
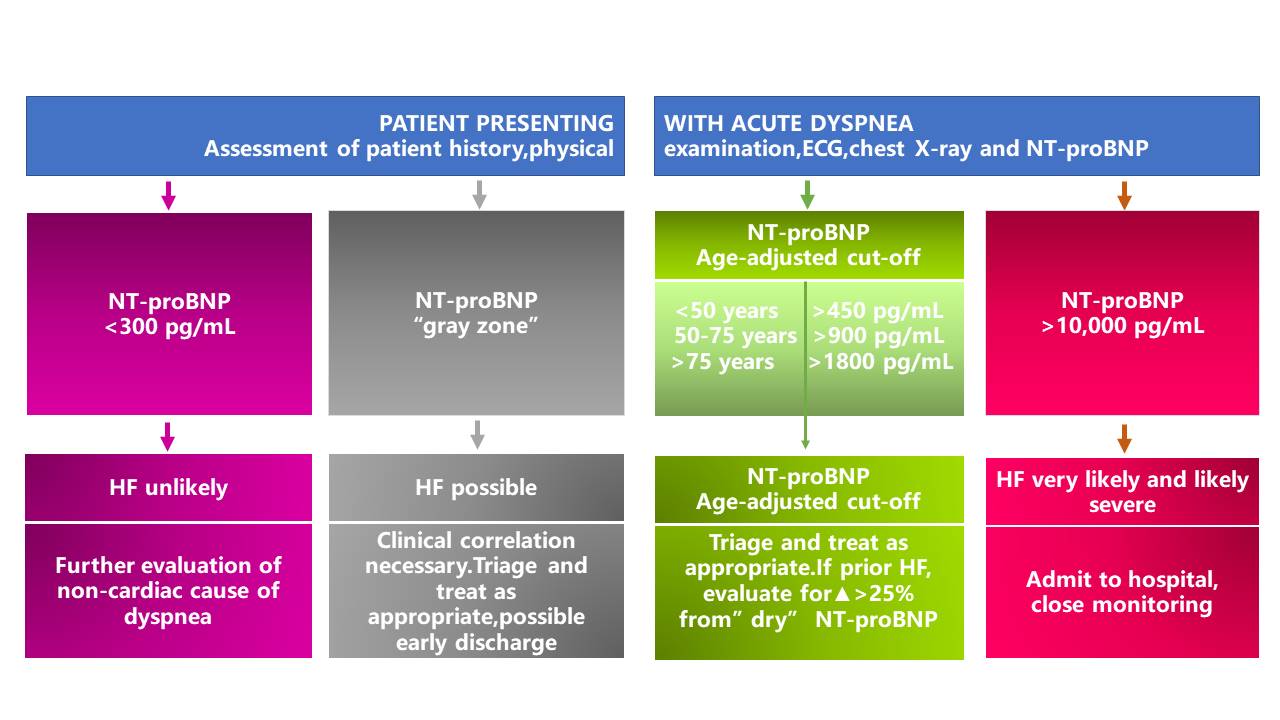
*The area between the rule-out (<300pg/mL) and the rule-in (age-ajusted) cut-off values is designated as the "gray zone".
NT-proBNP in the evaluation and triage of ED patients with acute dyspnea (4)
In primary care, NT-proBNP is particularly useful to guide referral of symptomatic chronic HF to specialist care because it excludes suspected left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Compared with NT-proBNP values in patients with acute HF, lower values are expected in ambulatory chronic HF patients. International guidelines recommend a single low cut-off of 125pg/mL to rule out HF for patients presenting with non-acute symptoms. However peer-reviewed literature supports the use of age-dependent cut-offs to adjust for loss of specificity in such settings(5).
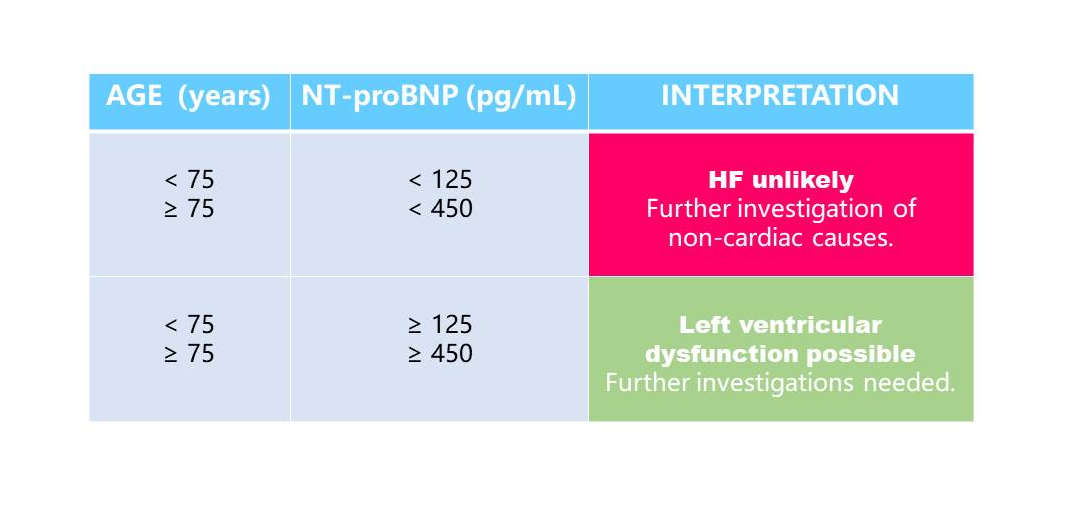
NT-proBNP in the primary care setting
Clinical significance:
Early elimination/diagnosis of heart failure, identification of causes of acute and chronic dyspnea Risk classification of patients with heart failure, prediction of adverse outcomes Efficacy monitoring, treatment guidance and prognosis evaluation for patients with heart failure
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
References:
1. Moe G.W, Howlett J, Januzzi JL, et al. Primary results of the Canadian prospective randomized multicenter IMPROVE-CHF study. Circulation 2007;115: 3103-3110.
2. McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, et al.; ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1787-847
3. Januzzi JL, van Kimmenade R, et al. the International Collaborative of NT-proBNP Study. Eur Heart J. 2006 ;27:330-7.
4. Januzzi JL, Chen-Tournoux AA, Moe G. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101 (Suppl.):29A-38A.
5. Hildebrandt P, Collinson PO, et al. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:1881-9.
SPECIFICATION
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | <75 years old, NT-proBNP≤300 pg/ml, ≥75 years old, NT-proBNP≤450 pg/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

 Request
Request
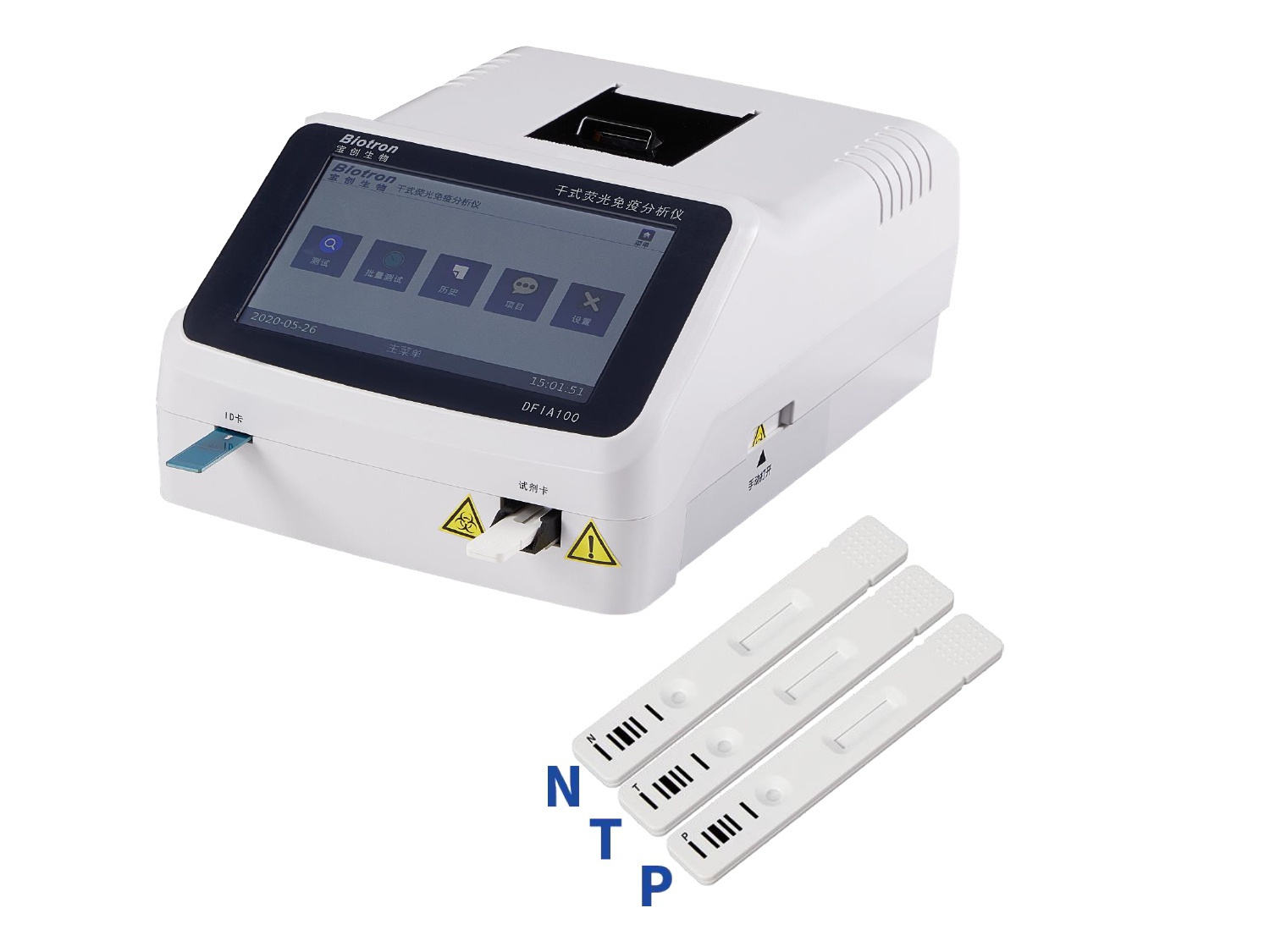
Applicable Instrument

CATALOGS