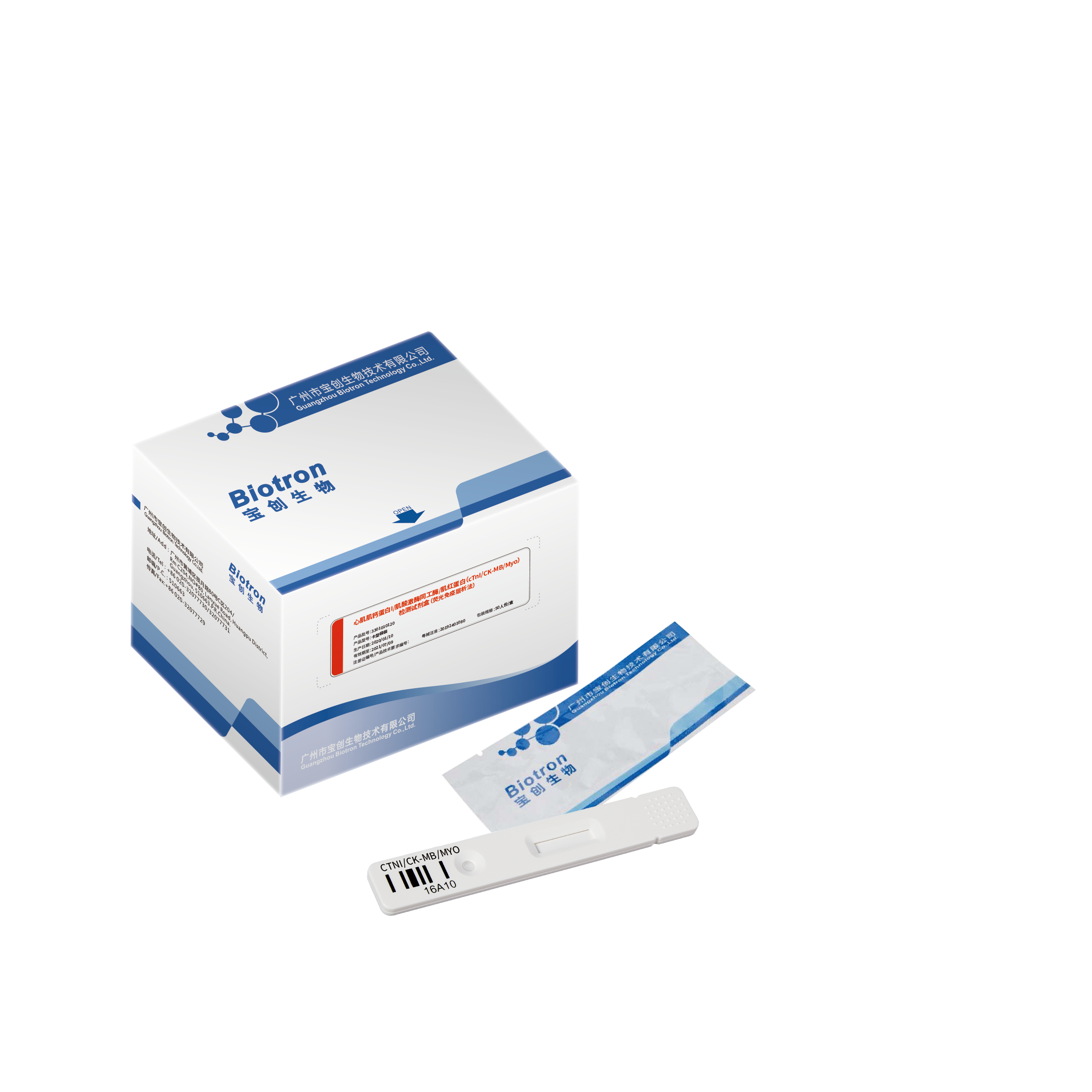
cTnl/CK-MB/Myo Rapid Test Kit
The reagent is used to quantitatively detect the content of cardiac troponin I, creatine kinase isoenzyme, and myoglobin in human serum, plasma or whole blood samples in vitro, and is mainly used for clinical auxiliary diagnosis of myocardial infarction.
Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
DESCRIPTION
Successfully obtained in the EU CE access certification
Passed ISO13485 certification
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and it incurs huge healthcare expenditures [1-4]. In the United States alone, 683,000 discharge occurrences resulting from ACS were reported in 2009 [5,6]. Remarkably, 1,190,000 secondary discharges were associated with ACS, of which 829,000 were attributed to myocardial infarction (MI) alone [5,6]. ACS is caused by the sudden obstruction of a coronary artery. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of ACS continues to be a diagnostic challenge in medicine, The highest risk of fatality occurs within the initial hours of onset of AMI. Thus, early diagnosis of cardiac ischemia is critical for the effective management of patients with AMI. Improper diagnosis of patients with chest pain often leads to inappropriate admission of patients without AMI and vice versa. In addition to clinical history, physical examination, accurate electrocardiogram findings and assessment of cardiac biomarkers have an important role in the early diagnosis of acute ischemia.
Myocardial Injury Marker:
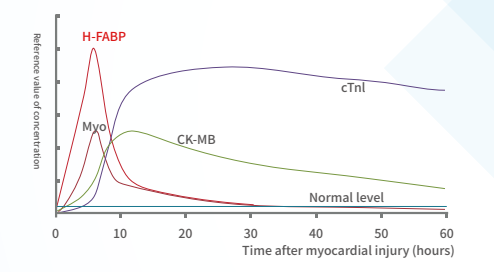
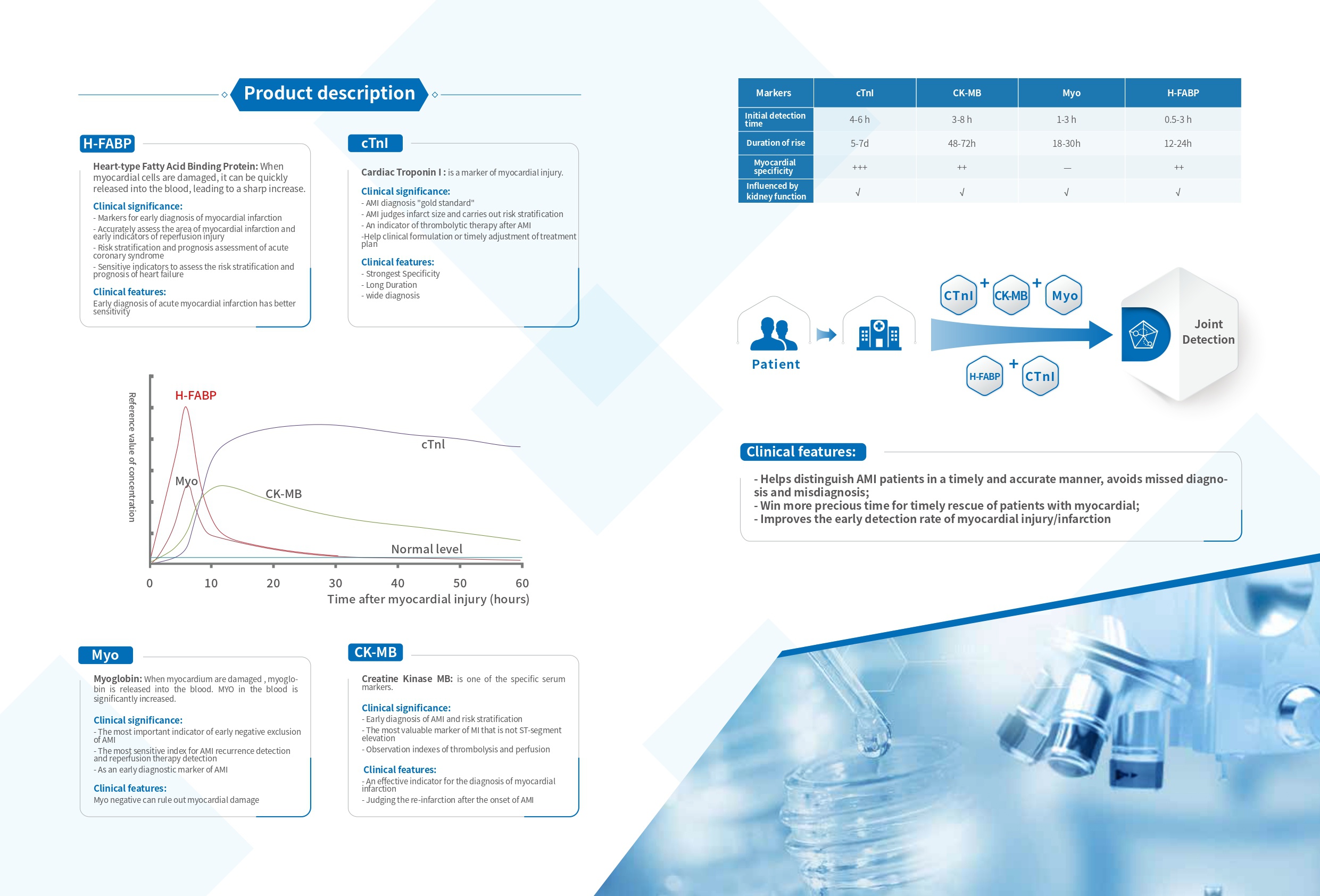
H-FABP: It is a small-molecule soluble protein that is abundant in the cytoplasm of myocardium, but when myocardial cells are damaged, it can be quickly released into the blood, leading to a sharp increase in the level of H-FABP in the blood high.H-FABP can be used as a predictive biomarker of mortality following acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
CTnI: It is a contractile protein that exists only in the myocardium. It is one of the three subunits of troponin complex (I, T, C), and combines with tropomyosin in the filaments of myofibrils to form actin.
Myo: Mainly present in the myocardium and skeletal muscle. When skeletal muscle and myocardium are damaged (acute myocardial infarction), excessive exercise and muscle diseases, myoglobin is released into the blood.The levels of MYO can therefore not be used as a single diagnostic marker, but in conjunction with the troponins or CK-MB. Thus, serum levels of MYO can be used to rule out, rather than diagnose, myocardial infarction (46).
CK-MB: a form of creatine kinase isoenzyme, which mainly exists in the myocardium. It is one of the important markers of myocardial injury and can effectively diagnose acute myocardial infarction.
Joint detection
The combined detection of the three items of myocardial infarction helps distinguish AMI patients in a timely and accurate manner, minimizes the damage, avoids missed diagnosis and misdiagnosis, and can win more precious time for timely rescue of patients with myocardial infarction.
Multi-index combined detection can improve the detection rate and accuracy of myocardial injury, reduce the missed diagnosis rate, and reduce doctor-patient disputes.
Clinical significance:
Combined detection for early diagnosis and risk stratification of acute myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction area estimation differential diagnosis of chest pain Prognostic evaluation of ACS
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
SPECIFICATION
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | cTnI≤0.3ng/ml,Myo≤58ng/ml,CK-MB≤5ng/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

 Request
Request
Applicable Instrument

CATALOGS
 2 pages
2 pages