


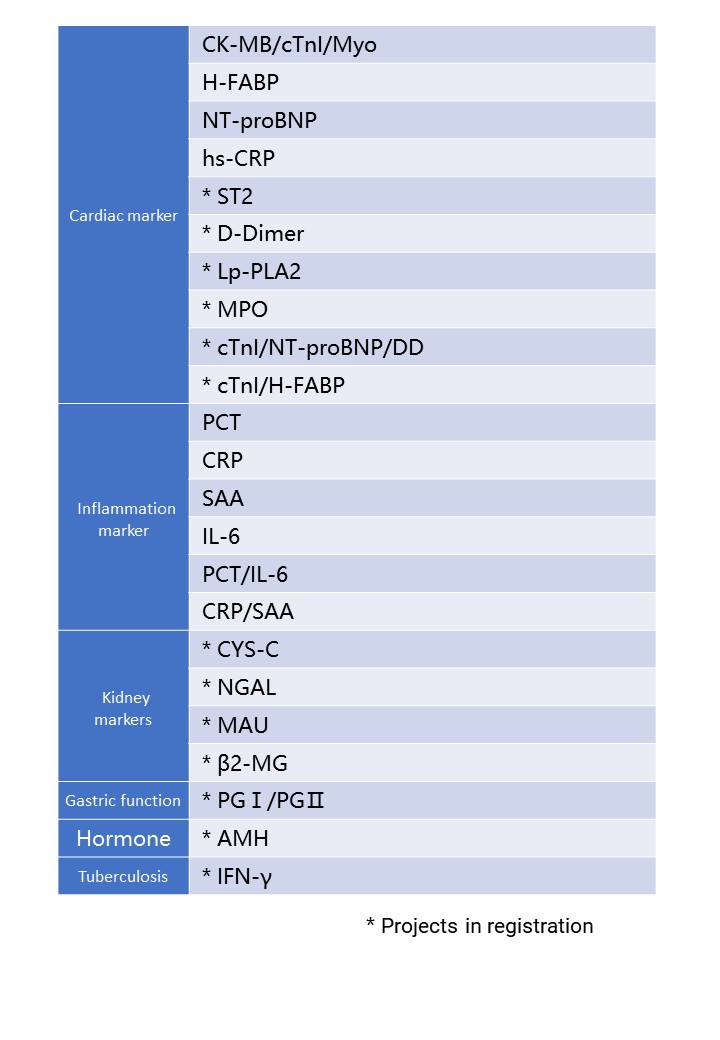
Cooperate with special single reagent strips to realize the quantitative detection of a series of immunoassay items.
Supports single or multiple biomarkers for simultaneous detection and quantitative detection of a series of immunoassays
Product Model:DFIA300
Detection channel: 3 channels
Detection principle: dry fluorescence immunoassay
Sample type and blood volume requirements: serum, plasma, whole blood; ≤100µl
Display: 8-inch touch screen
Result transmission: support LIS transmission results
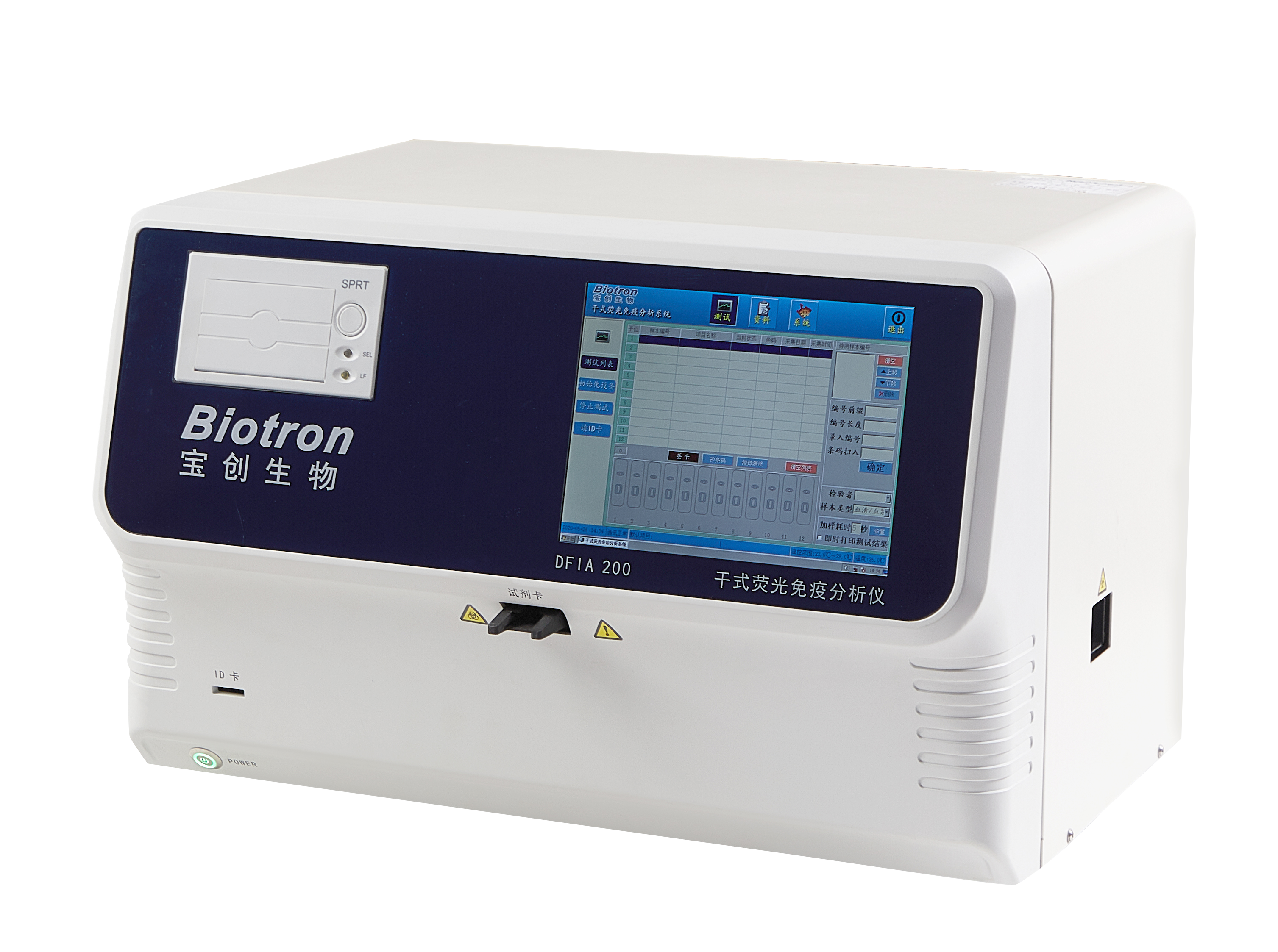


- Rotating 12-channel instrument with multi-sample batch detection capability
- Applicable to a variety of sample types
- Easy to operate, with a single reagent strip to automatically complete rapid quantitative detection
Cooperate with special single reagent strips to realize the quantitative detection of a series of immunoassay items.
| Product model | DFIA200 |
| Detection channel | 12-channel |
| Detection principle | dry fluorescence immunoassay |
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Blood volume requirements | ≤100µl |
| Detection speed | ≤ 15 minutes |
| Display | 8-inch color screen |
| Result transmission | support LIS transmission result |
| Detection method | support one card one item, one card multiple data processing |


- Single-channel instrument, light and compact
- Applicable to a variety of sample types
- Easy to operate, with a single reagent strip to automatically complete rapid quantitative detection
Cooperate with special single reagent strips to realize the quantitative detection of a series of immunoassay items.
| Product model | DFIA100 |
| Detection channel | single channel |
| Detection principle | dry fluorescence immunoassay |
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Blood volume requirements | ≤100µl |
| Detection speed | ≤ 15 minutes |
| Display | 7-inch touch screen |
| Result transmission | support LIS transmission result |
| Detection method | support one card one item, one card multiple data processing |




Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Expected usage:
The reagent is used for clinical in vitro quantitative detection of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) content in human serum, plasma, or whole blood samples, and is mainly used clinically for auxiliary diagnosis of bacterial infectious diseases.
Clinical significance:
In the inflammatory response, IL-6 rises earlier than other indicators and lasts for a long time, so it can be used to assist in the early diagnosis of acute infection. Dynamic observation of IL-6 levels also helps to understand the progress of infectious diseases and the response to treatment.
Applicable departments:
Laboratory department, emergency department, pediatrics/neonatology, infection department, respiratory department, neurology, surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, oncology, ICU, CCU, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | IL-6 ≤7pg/mL |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (3 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Expected usage:
The reagent is used for clinical in vitro quantitative detection of C-reactive protein (CRP) content in human serum, plasma or whole blood. C-reactive protein is mainly used as a non-specific inflammation indicator.
Clinical significance:
Identify bacterial or viral infections and use it for dynamic observation of antibiotic efficacy. Monitor changes in the condition and postoperative infection. Disease course detection and prognosis judgment.
Applicable departments:
Laboratory department, emergency department, pediatrics/neonatology, infection department, respiratory department, neurology, surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, oncology, ICU, CCU, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 3min |
| Reference range | hs-CRP≤1.0mg/L,CRP≤10 mg/L |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature.
Expected usage:
The reagent is used for clinical in vitro quantitative detection of procalcitonin (PCT) content in human serum, plasma, or whole blood samples, and is mainly used clinically for auxiliary diagnosis of bacterial infectious diseases.
Clinical significance:
Assist in the differential diagnosis of severe bacterial infections, sepsis and multiple organ failure Evaluation of the degree of infection and prognosis Instruct the rational use of antibiotics and the monitoring of efficacy.
Applicable departments:
Laboratory department, emergency department, pediatrics/neonatology, infection department, respiratory department, neurology, surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, oncology, ICU, CCU, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | PCT ≤ 0.5ng/mL |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 50 tests/box |


Quick detection of single reagent (10 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
One card dual inspection, high sensitivity, wide linear range
Expected usage:
The reagent is used for clinical in vitro quantitative detection of C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A content in human serum samples, mainly as non-specific inflammation indicators.
Clinical significance:
Differential diagnosis index for bacterial infection and viral infection
Applicable departments:
Laboratory department, emergency department, pediatrics/neonatology, infection department, respiratory department, neurology, surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, oncology, ICU, CCU, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | CRP≤10mg/L,SAA≤10mg/L |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature.
Expected usage:
The reagent is used for clinical in vitro quantitative detection of procalcitonin (PCT) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) content in human serum, plasma, or whole blood samples, PCT is mainly used in clinical diagnosis of bacterial infections. IL-6 is mainly used to monitor the immune status and inflammation of the body.
Clinical significance
Increasing the rate of early diagnosis of infection is a necessary test item for early warning and rapid diagnosis of sepsis and to guide the correct use of antibiotics.
Applicable departments:
Laboratory department, emergency department, pediatrics/neonatology, infection department, respiratory department, neurology, surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, oncology, ICU, CCU, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | PCT ≤ 0.5ng/mL,IL-6≤7pg/mL |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

Quick detection of single reagent (10 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Expected usage:
The reagent is used for clinical in vitro quantitative detection of SAA content in human serum, mainly as a non-specific inflammation indicator.
Clinical significance:
Sensitive indicators to identify viral infections, combined with CRP and blood routine testing, can be used for early differential diagnosis, dynamic observation of curative effects and guidance of medication. Differential diagnosis of infectious diseases in children.
Applicable departments:
Laboratory department, emergency department, pediatrics/neonatology, infection department, respiratory department, neurology, surgery, cardiology, gastroenterology, oncology, ICU, CCU, etc.
| Sample type | serum |
| Report time | 10min |
| Reference range | SAA≤10mg/L |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |



Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Lp-PLA2: an emerging biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intravascular highly specific inflammatory factors
- Independent risk predictors of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
Lp-PLA2 induces an increase in plaque instability, making the plaque fragile and ruptured, leading to thrombosis and ischemic stroke. In addition, high levels of Lp-PLA2 predict increased instability of atherosclerotic plaques, more prone to rupture, and increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular malignant events.Schematic diagram of Lp-PLA2 is shown in Figure 1.
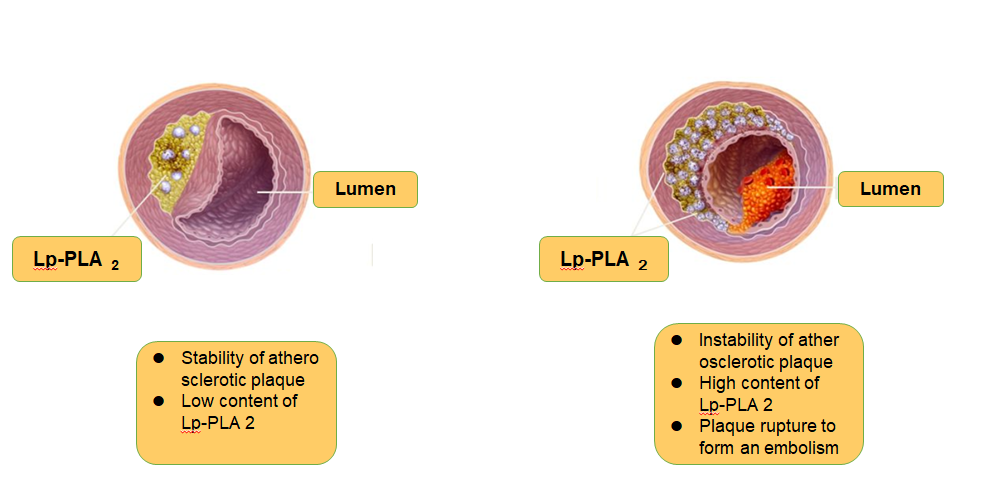
Figure 1
Schematic diagram of Lp-PLA2 and plaque stability
References:
The international recognition and importance of Lp-PLA2 is gradually increasing, and it is recommended that Lp-PLA2 be used in various aspects of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as screening, differential diagnosis, risk assessment, treatment and prognosis.Guideline Recommendation Table is shown in Figure 2.
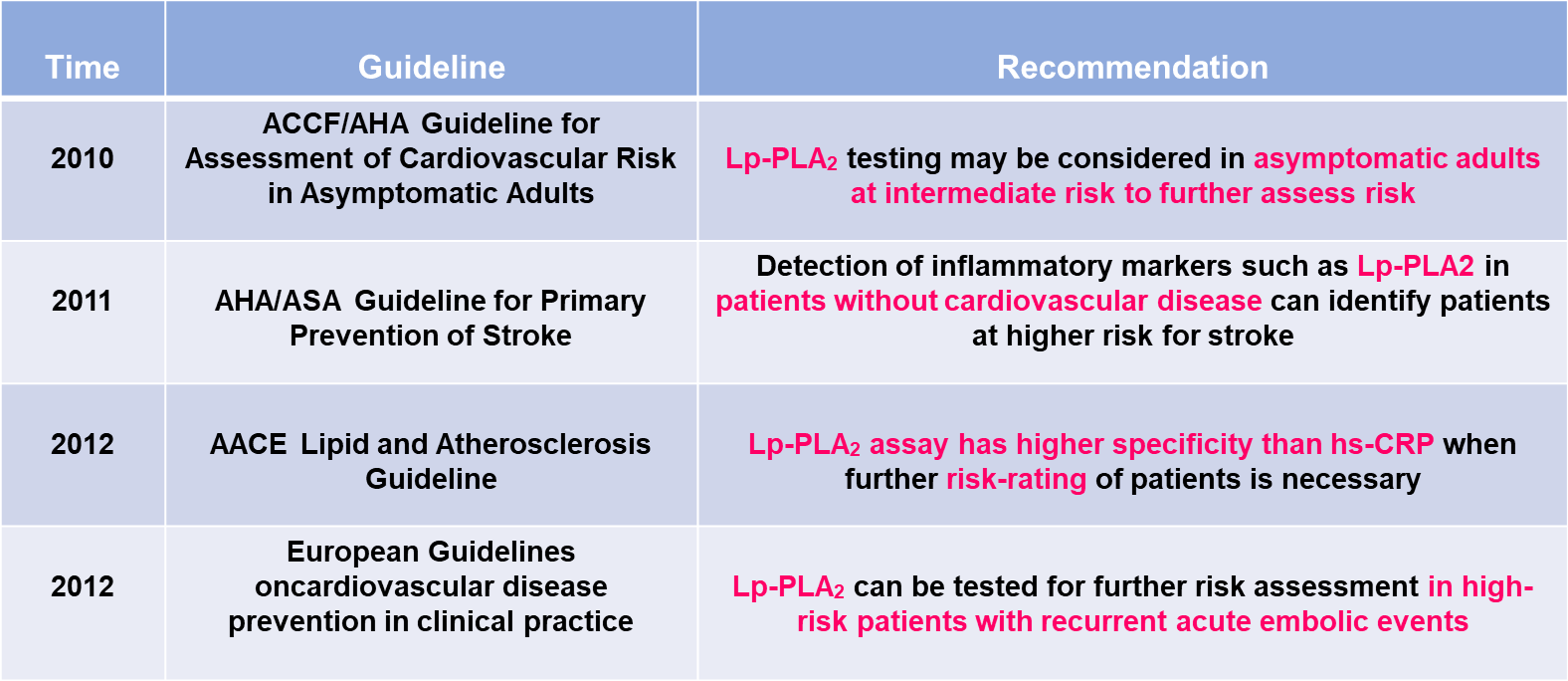
Figure 2
Lp-PLA2 Guideline Recommendation Table
Clinical significance:
-Dynamic monitor of the degree of inflammation in the vascular endothelium and atherosclerotic plaques
-Risk estimation for coronary heart disease and stroke
-Estimated risk of recurrence for various cardiovascular embolisms (stroke)
-Efficacy assessment , the decreased level of Lp-PLA2 is positively correlated with the lipid-lowering effect of statins
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, cardiac surgery, neurology, veteran department, endocrinology, laboratory department, physical examination center
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood;
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and it incurs huge healthcare expenditures [1-4]. In the United States alone, 683,000 discharge occurrences resulting from ACS were reported in 2009 [5,6]. Remarkably, 1,190,000 secondary discharges were associated with ACS, of which 829,000 were attributed to myocardial infarction (MI) alone [5,6]. ACS is caused by the sudden obstruction of a coronary artery. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of ACS continues to be a diagnostic challenge in medicine, The highest risk of fatality occurs within the initial hours of onset of AMI. Thus, early diagnosis of cardiac ischemia is critical for the effective management of patients with AMI. Improper diagnosis of patients with chest pain often leads to inappropriate admission of patients without AMI and vice versa. In addition to clinical history, physical examination, accurate electrocardiogram findings and assessment of cardiac biomarkers have an important role in the early diagnosis of acute ischemia.
A marker of Myocardial Injury:
H-FABP: It is a small-molecule soluble protein that is abundant in the cytoplasm of myocardium, but when myocardial cells are damaged, it can be quickly released into the blood, leading to a sharp increase in the level of H-FABP in the blood high.H-FABP can be used as a predictive biomarker of mortality following acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
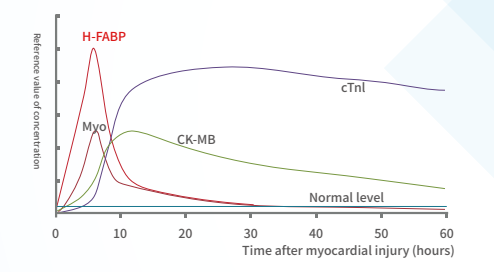
Clinical significance:
Detection for the early diagnosis and risk stratification of acute myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction area estimation Differential diagnosis of chest pain Prognostic evaluation of ACS
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | H-FABP≤7ng/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and it incurs huge healthcare expenditures [1-4]. In the United States alone, 683,000 discharge occurrences resulting from ACS were reported in 2009 [5,6]. Remarkably, 1,190,000 secondary discharges were associated with ACS, of which 829,000 were attributed to myocardial infarction (MI) alone [5,6]. ACS is caused by the sudden obstruction of a coronary artery. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of ACS continues to be a diagnostic challenge in medicine, The highest risk of fatality occurs within the initial hours of onset of AMI. Thus, early diagnosis of cardiac ischemia is critical for the effective management of patients with AMI. Improper diagnosis of patients with chest pain often leads to inappropriate admission of patients without AMI and vice versa. In addition to clinical history, physical examination, accurate electrocardiogram findings and assessment of cardiac biomarkers have an important role in the early diagnosis of acute ischemia.
Myocardial Injury Marker:
H-FABP: It is a small-molecule soluble protein that is abundant in the cytoplasm of myocardium, but when myocardial cells are damaged, it can be quickly released into the blood, leading to a sharp increase in the level of H-FABP in the blood high.H-FABP can be used as a predictive biomarker of mortality following acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
CTnI: It is a contractile protein that exists only in the myocardium. It is one of the three subunits of troponin complex (I, T, C), and combines with tropomyosin in the filaments of myofibrils to form actin.
Myo: Mainly present in the myocardium and skeletal muscle. When skeletal muscle and myocardium are damaged (acute myocardial infarction), excessive exercise and muscle diseases, myoglobin is released into the blood.The levels of MYO can therefore not be used as a single diagnostic marker, but in conjunction with the troponins or CK-MB. Thus, serum levels of MYO can be used to rule out, rather than diagnose, myocardial infarction (46).
CK-MB: a form of creatine kinase isoenzyme, which mainly exists in the myocardium. It is one of the important markers of myocardial injury and can effectively diagnose acute myocardial infarction.

Joint detection
The combined detection of the three items of myocardial infarction helps distinguish AMI patients in a timely and accurate manner, minimizes the damage, avoids missed diagnosis and misdiagnosis, and can win more precious time for timely rescue of patients with myocardial infarction.
Multi-index combined detection can improve the detection rate and accuracy of myocardial injury, reduce the missed diagnosis rate, and reduce doctor-patient disputes.
Clinical significance:
Combined detection for early diagnosis and risk stratification of acute myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction area estimation differential diagnosis of chest pain Prognostic evaluation of ACS
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | cTnI≤0.3ng/ml,Myo≤58ng/ml,CK-MB≤5ng/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |



Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
ST2: a novel biomarker for heart failure
ST2 is a member of the interleukin-I(IL-1)receptor family. When the heart continues to be under pressure, the expression of ST2 increases, which indirectly promotes myocardial hypertrophy and myocardial fibrosis, affects cardiac function, and greatly increases the readmission and mortality of patients with heart failure.
ST2 is released when cardiomyocytes stretch, neutralizing its ligand IL-33 (1, 2). It is also associated with inflammation during the MI and HF (3). As a decoy receptor of IL-33 receptor (ST2L), an appropriate amount of sST2 can prevent uncontrolled inflammation. However, redundant sST2 could also block the advantageous biological effect of IL-33 due to its competitive role against ST2L, which will eventually cause HF (3). Recently, sST2 is frequently reported to be associated with CVDs, especially HF (5–6). The ST2 pathway in CVD is shown in Figure 1.
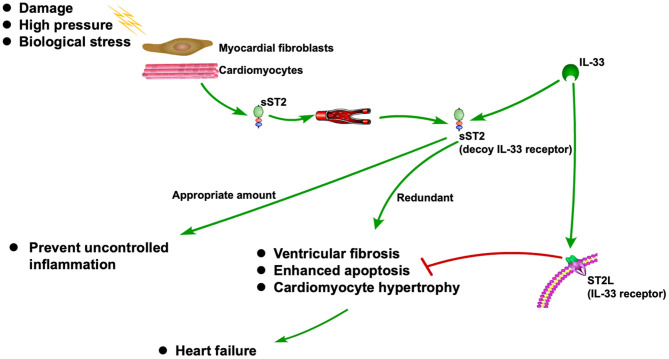
Figure 1
ST2 pathway in CVD
Biomarkers have made a significant contribution to the diagnosis and prognosis of disease. Although strongly associated with inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, ST2 has also been found to play a role in the diagnosis and prognosis of CVD (4, 7). As one of the isoforms of ST2, sST2 has recently become a promising prognostic indicator for patients diagnosed with HF and a useful tool for risk stratification (8). Due to its prognostic value, sST2 was recommended by the American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) as an important biomarker for monitoring HF patients in 2013 (9).
ST2 yielded strong, independent predictive value for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, and HF hospitalization in chronic HF, and deserves consideration to be part of a multimarker panel together with NT-proBNP and hs-TnT.
Clinical significance:
• Auxiliary diagnosis of heart failure
• For monitoring the efficacy of heart failure
• For risk stratification and prognostic risk assessment of heart failure
Applicable departments:
Emergency department, cardiac surgery, cardiology, chest pain center, Clinical Laboratory, ICU, CCU.
References:
1. Weinberg EO, Shimpo M, De Keulenaer GW, MacGillivray C, Tominaga S, Solomon SD, et al. Circulation. (2002)
3. Marino R, Magrini L, Orsini F, Russo V, Cardelli P, Salerno G, et al. Ann Lab Med. (2017)
4. Oshikawa K, Kuroiwa K, Tago K, Iwahana H, Yanagisawa K, Ohno S, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2001)
5. Dudek M, Kałuzna-Oleksy M, Migaj J, Straburzyńska-Migaj E. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2020)
6. McCarthy CP, Januzzi JL, Jr. Soluble ST2 in Heart Failure. Heart Fail Clin. (2018)
| Sample type | serum, plasma |
| Report time | 15min |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry, the validity period is 18 months |
| Specifications | 50 tests/box |

Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Heart failure (HF) biomarkers have dramatically impacted the way HF patients are evaluated and managed. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP) are the gold standard biomarkers in determining the diagnosis and prognosis of HF, and studies on natriuretic peptide-guided HF management look promising.
NT-proBNP: A gold standard for Heart Failure
International guidelines recommend the use of B-type natriuretic peptide testing in the diagnostic workup of Heart Failure (HF) in both acute and non-acute patient presentation(2).
In the emergency department (ED), NT-proBNP is particularly useful for the triage of patients with acute dyspnea and suspected acute HF. It is highly sensitive and specific for exclusion (single rule-out cut-off value of 300 pg/mL) or confirmation of acute HF (age-adjusted rule-in cut-off values) (3).
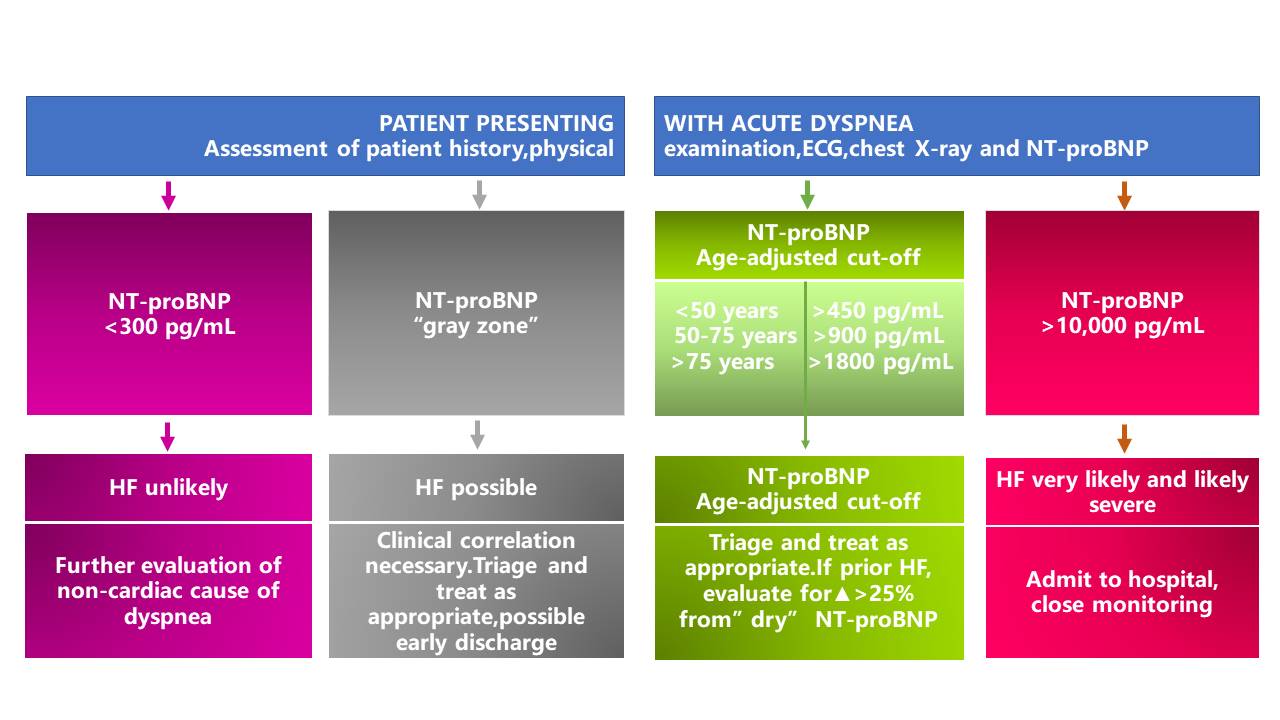
*The area between the rule-out (<300pg/mL) and the rule-in (age-ajusted) cut-off values is designated as the "gray zone".
NT-proBNP in the evaluation and triage of ED patients with acute dyspnea (4)
In primary care, NT-proBNP is particularly useful to guide referral of symptomatic chronic HF to specialist care because it excludes suspected left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Compared with NT-proBNP values in patients with acute HF, lower values are expected in ambulatory chronic HF patients. International guidelines recommend a single low cut-off of 125pg/mL to rule out HF for patients presenting with non-acute symptoms. However peer-reviewed literature supports the use of age-dependent cut-offs to adjust for loss of specificity in such settings(5).
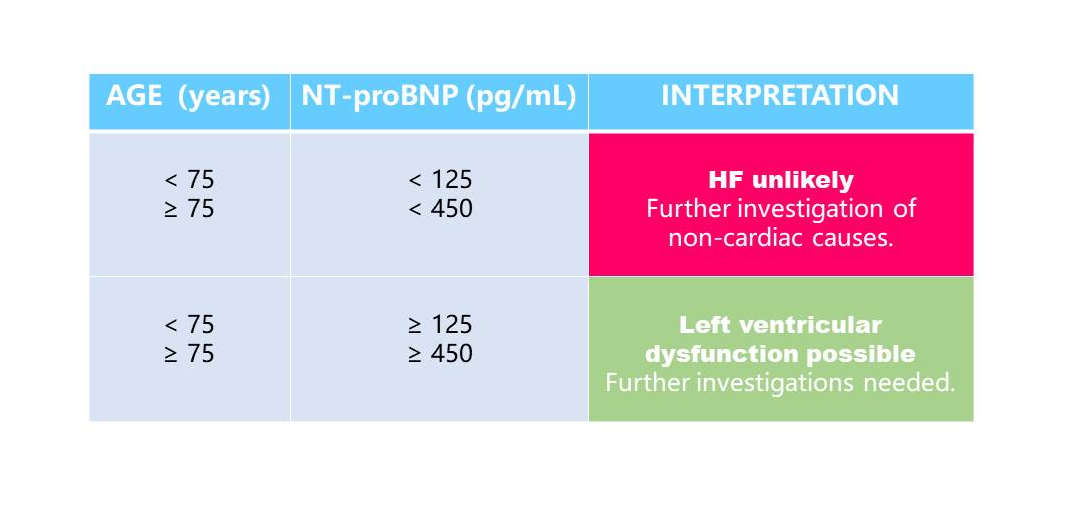
NT-proBNP in the primary care setting
Clinical significance:
Early elimination/diagnosis of heart failure, identification of causes of acute and chronic dyspnea Risk classification of patients with heart failure, prediction of adverse outcomes Efficacy monitoring, treatment guidance and prognosis evaluation for patients with heart failure
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
References:
1. Moe G.W, Howlett J, Januzzi JL, et al. Primary results of the Canadian prospective randomized multicenter IMPROVE-CHF study. Circulation 2007;115: 3103-3110.
2. McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, et al.; ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1787-847
3. Januzzi JL, van Kimmenade R, et al. the International Collaborative of NT-proBNP Study. Eur Heart J. 2006 ;27:330-7.
4. Januzzi JL, Chen-Tournoux AA, Moe G. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101 (Suppl.):29A-38A.
5. Hildebrandt P, Collinson PO, et al. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:1881-9.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | <75 years old, NT-proBNP≤300 pg/ml, ≥75 years old, NT-proBNP≤450 pg/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |




Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Can be tested at any time in menstrual cycle
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
AMH: a marker for ovarian reserve
AMH is secreted by preantral follicles and small antral follicles in the ovary, and its level is directly related to the number of follicles in the ovary. Schematic model of AMH actions in the ovary that is shown in Figure 1.
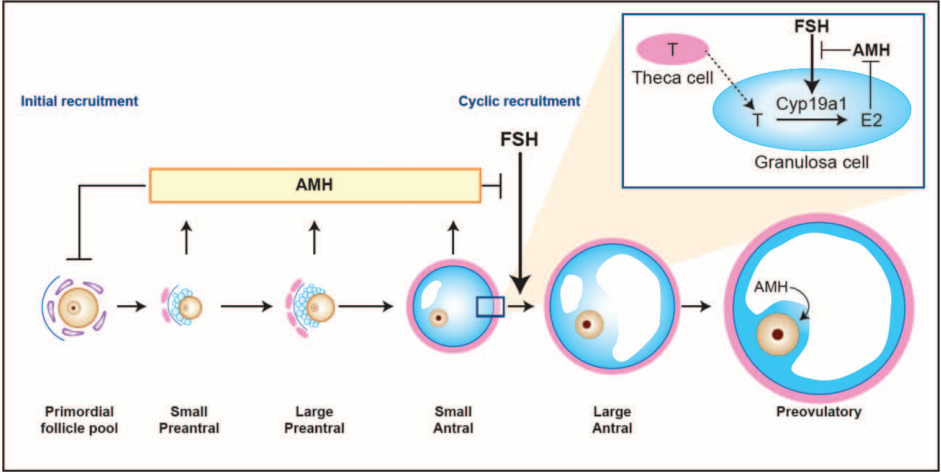
Figure 1
Schematic model of AMH actions in the ovary
AMH is an indicator familiar to experts in gynecological endocrinology and assisted reproductive technology and is commonly used in ovarian reserve, ovarian responsiveness prediction, and PCOS disease diagnosis. AMH is the earliest hormone to change with age and is therefore a more accurate predictor of ovarian reserve in women at an earlier stage.
ESHRE consensus on the definition of‘poor response’to ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization.
AMH had the best sensitivity and specificity for predicting ovarian response.(Figure 2)
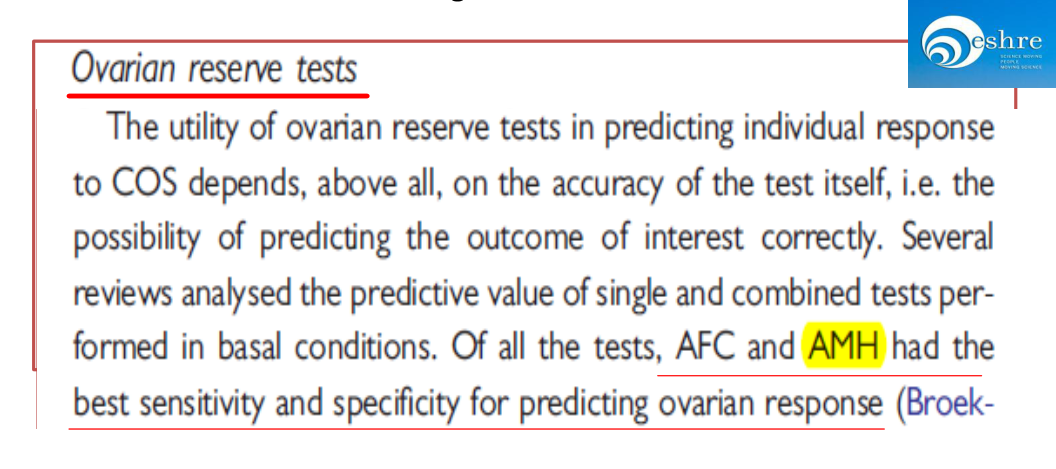
Figure 2
Clinical significance:
• Evaluation of ovarian reserve
• Prediction of reproductive ovarian reactivity
• Predicting menopause
• Auxiliary diagnosis of ovarian related diseases in women (PCOS/POI)
Applicable departments:
Physical examination center, reproductive center, gynecology, oncology, pediatrics
References:
1.NICE Clinical Guideline 156, 2013
2.Visser JA.et,al. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Jan 10;8(6):331-41.
3.Fleming R.et,al.Reprod Biomed Online. 2015 Oct;31(4):486-96.
4.Dumont A.et,al. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018 Dec;25(6):377-384.
| Sample type | Serum, plasma ,whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry, the validity period is 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box ,50 tests/box |


Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
→ Female reproduction
Inhibin B is secreted by the granulosa cells of small antral follicles in women and directly reflect ovarian reserve.
→ Male reproduction
Inhibin B is produced by Sertoli cells in males, and its level reflects the function of the entire testicular tissue . Inhibin B is the best and most direct marker for evaluating male spermatogenesis.
INH-B:a novel marker of spermatogenesis
Subfertility affects about 15% of all couples. Assessment of spermatogenesis has a central role in the evaluation of the subfertile couple. Recently, the serum inhibin B level has emerged as a sensitive endocrine marker of spermatogenesis. The serum inhibin B level has been shown to be associated with classical markers of spermatogenesis, particularly testicular histology, and to be the most accurate endocrine marker of spermatogenesis. Schematic representation of the hypothala-mic-pituitary-testis axis in adulthood that is shown in Figure 1.
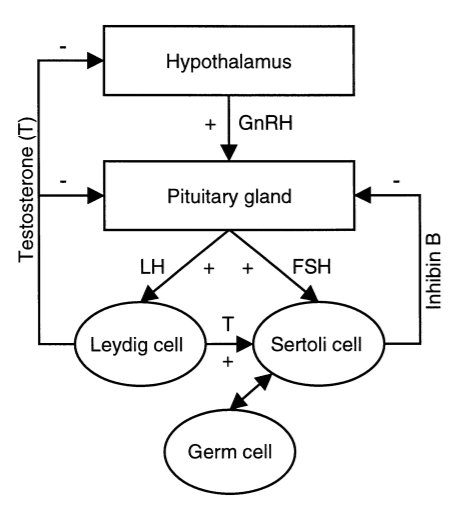
Figure 1
Schematic representation of the hypothala-mic-pituitary-testis axis in adulthood
Hypothalamic GnRH stimulates the pituitary secretion of FSH and LH. LH stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone (T). FSH and testosterone directly stimulate Sertoli cells, which in turn, regulate germ cell development. GnRH is under negative feedback control by testosterone, while pituitary secretion of LH and FSH is under feedback control by testosterone, and inhibin B causes selective inhibition of FSH production. Inhibin B is produced by Sertoli cells in interaction with specific germ cell types. GnRH = gonadotrophin-releasing hormone; FSH = follicle-stimulating hormone; LH = luteinising hormone.
Clinical significance:
• Analysis of male infertility
• Application of Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESE) in Assisted Reproductive Technology
• Auxiliary diagnosis of childhood precocious puberty
Applicable departments:
Physical examination center, reproductive center, gynecology, oncology, pediatrics
References:
1.NICE Clinical Guideline 156, 2013.
2.Visser JA.et,al. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012 Jan 10;8(6):331-41.
3.Fleming R.et,al.Reprod Biomed Online. 2015 Oct;31(4):486-96.
4.Dumont A.et,al. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018 Dec;25(6):377-384.
5.Pierik FH.et,al.Ann Med. 2003;35(1):12-20.
| Sample type | Serum, plasma ,whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry, the validity period is 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box ,50 tests/box |




Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
PG and G17 serum levels in combination with gastroscopy was a powerful approach to diagnosing early-stage GC.
Gastroscopy followed by examinations of biopsy specimens is the gold standard for diagnosing gastric cancer (GC). A disadvantage of this method is that it is invasive and causes discomfort and pain, making it an undesirable procedure for diagnostics. Several attempts have been made to detect precancerous lesions and early-stage GC in high incidence areas by examining serum levels of pepsinogen (PG) and gastrin-17 (G17), which could offer an effective and non-invasive alternative to traditional gastroscopy for diagnosing GC.1–3 . Three Introductions to Stomach Function is shown in Figure 1.
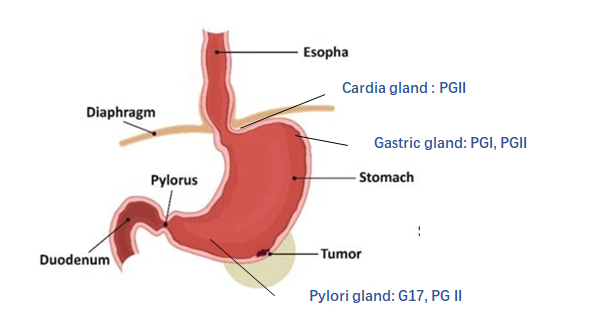
Figure 1
Three Introductions to Stomach Function
PGI Mainly secreted by chief cells and mucous neck cells of fundic glands. PGI was negatively correlated with atrophic gastritis in the fundus and corpus, and positively correlated with peptic ulcer.
PGII It is secreted by all gastric glands and duodenum. PGII is positively correlated with gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer and Hp infection.
PGR (PGI/PGII) Decreased PGI and normal PGII: The progressive decrease of PGR is related to the progress of gastric mucosal atrophy and gastric fundus.
G17 is secreted by G cells in the gastric antrum, and there is a strict negative feedback mechanism with gastric acid level, which is negatively correlated with atrophic gastritis of the gastric antrum.
Clinical significance:
- Screening for gastric ulcer, atrophic gastritis, and early gastric cancer
- Determination index of recurrence after gastric cancer resection
- Determination index for recurrence and cure of peptic ulcer
- Dynamic monitoring of individual gastric mucosal function
- Stomach Health Checkup for Physical Examination People
Applicable departments:
Gastroenterology, oncology, physical examination center, surgery
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |




Applicable to various sample types of urine
Rapid detection of single reagent (10 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to the abnormality of kidney structure and function (including abnormal blood, urine, histology and imaging examination) within 3 months of disease course. resulting in clinical syndromes with different clinical manifestations.
In recent years, some new and more sensitive biomarkers of AKI have been discovered in clinical and laboratory studies, which can not only diagnose AKI before serum creatinine rises, but also provide help for the etiological diagnosis of AKI.
NGAL The best index for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury
CYS-C The best endogenous index of glomerular filtration rate
β2-MG Monitoring indicators of proximal tubule function
MAU Sensitive indicator of early or mild kidney injury
Microalbuminuria (MAU)
MAU is the most sensitive and reliable diagnostic indicator for early detection of renal disease. When the kidney is damaged, the urinary albumin excretion rate exceeds the normal range, which reflects the damage of glomerular filtration function and renal tubular reabsorption function. Combined with the incidence, symptoms and medical history statement, it can be more accurate to diagnose the condition.
Clinical significance:
- Important indicators for early diagnosis of hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
- Early indications of changes in the kidneys and cardiovascular system
- Auxiliary diagnosis for glomerular injury
- Surveillance of pregnancy-induced hypertensive kidney injury
Applicable departments:
Nephrology, emergency, interventional, ICU, cardiology, surgery
| Sample type | urine |
| Report time | 10 min |
| Reference range | |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma, whole blood and urine
Rapid detection of single reagent (10 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to the abnormality of kidney structure and function (including abnormal blood, urine, histology and imaging examination) within 3 months of disease course. resulting in clinical syndromes with different clinical manifestations.
In recent years, some new and more sensitive biomarkers of AKI have been discovered in clinical and laboratory studies, which can not only diagnose AKI before serum creatinine rises, but also provide help for the etiological diagnosis of AKI.
NGAL The best index for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury
CYS-C The best endogenous index of glomerular filtration rate
β2-MG Monitoring indicators of proximal tubule function
MAU Sensitive indicator of early or mild kidney injury
β2 Microglobulin (β2-MG)
The synthesis rate of β2-MG in healthy people is very stable, and it is only decomposed and excreted by the kidneys, and is not affected by factors such as age, gender, and muscle. The increase of β2-MG in plasma reflects the impairment of glomerular filtration function or the increase of filtration load; the increase of β2-MG in urine indicates the increase of renal tubular damage or load.
Clinical application of blood β2-MG:
- For estimation of renal function disorders
a. Assessment of renal impairment in hypertension and diabetes
b. Dynamic observation and diagnosis of renal transplant rejection
- Prognosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of malignant tumor diseases
- Autoimmune disease assessment and efficacy monitoring
Clinical application value of urinary β2-MG
- Sensitive and specific method for the diagnosis of proximal convoluted tubule damage
- For the identification of upper and lower urinary tract infections
- Used to determine rejection of kidney transplantation, and a marked increase is seen several days before rejection
Applicable departments:
Nephrology, emergency, interventional, ICU, cardiology, surgery
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood,urine |
| Report time | 10min |
| Reference range | |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma, whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (5 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to the abnormality of kidney structure and function (including abnormal blood, urine, histology and imaging examination) within 3 months of disease course. resulting in clinical syndromes with different clinical manifestations.
In recent years, some new and more sensitive biomarkers of AKI have been discovered in clinical and laboratory studies, which can not only diagnose AKI before serum creatinine rises, but also provide help for the etiological diagnosis of AKI.
NGAL The best index for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury
CYS-C The best endogenous index of glomerular filtration rate
β2-MG Monitoring indicators of proximal tubule function
MAU Sensitive indicator of early or mild kidney injury
Cystatin C (CYS-C)
CYS-C is produced at a constant rate in the body and is almost completely filtered by the glomerulus. CYS-C in the blood is not affected by changes in inflammation, sex, muscle, and age, but its concentration varies with the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) changes.
Clinical significance:
- Reflects the functional level of glomerular filtration
- Early diagnosis and condition monitoring of kidney disease
- Renal function monitoring in patients with kidney transplantation and chemotherapy
- Early prevention and diagnosis of early renal damage in AKI high-risk population
- Renal function assessment in patients with cirrhosis
Applicable departments:
Nephrology, emergency, interventional, ICU, cardiology, surgery
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 5min |
| Reference range | |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma, whole blood and urine
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute kidney injury (AKI) refers to the abnormality of kidney structure and function (including abnormal blood, urine, histology and imaging examination) within 3 months of disease course. resulting in clinical syndromes with different clinical manifestations.
In recent years, some new and more sensitive biomarkers of AKI have been discovered in clinical and laboratory studies, which can not only diagnose AKI before serum creatinine rises, but also provide help for the etiological diagnosis of AKI.
NGAL The best index for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury
CYS-C The best endogenous index of glomerular filtration rate
β2-MG Monitoring indicators of proximal tubule function
MAU Sensitive indicator of early or mild kidney injury
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL)
NGAL is a member of the lipocalin family and normally maintains low levels in urine and blood. In the early stage (2h) of acute kidney injury (AKI), the level of NGAL in urine and blood increased significantly, and NGAL appeared before other indicators. Therefore, NGAL is one of the most effective biomarkers for the diagnosis of AKI, and its changes are earlier and more significant than traditional AKI diagnostic indicators.
Clinical significance:
- The best index for early diagnosis of AKI
- Chronic kidney disease, early detection of diabetic nephropathy
- Early detection and prognostic evaluation of AKI complicated by various operations
- Prognostic evaluation of kidney injury complicated by renal transplantation
- Early diagnosis of cardiovascular disease patients and ICU patients complicated with renal disease
Applicable departments:
Nephrology, emergency, interventional, ICU, cardiology, surgery
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood,urine |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |



For qualitatively detect BRAF gene V600E mutation (ie 1799T>A)
Evaluate gene mutation status by detecting DNA samples, assist in the diagnosis of thyroid cancer, and select tumor-targeted drugs for clinicians in patients with melanoma, colorectal cancer, thyroid cancer or lung cancer Provide reference for treatment.
Auxiliary diagnosis of thyroid cancer and select tumor-targeted drugs for clinicians in patients with melanoma, colorectal cancer, thyroid cancer or lung cancer Provide reference for treatment.
| Various sample types | paraffin-embedded pathological tissue, sectioned tissue, fresh tissue, frozen tissue |
| Easy to operate | without special equipment, 90min completion detection, detection closed tube, without subsequent processing |
| Reliable test results | intuitive and easy to interpret; high precision, CV≤5%; high sensitivity, can detect 1% of B-raf gene mutations |
Conventional fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument


- For in vitro quantitative detection of HBV DNA in human serum or plasma
- Response and treatment monitoring for antiviral therapy
For in vitro quantitative detection of HBV DNA in human serum or plasma
| High sensitivity | the lowest detection limit is 10 IU/ml; |
| Wide linear range | 20-2×109 IU/ml |
| Wide gene coverage | A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H |
| Set internal standard | can prevent false negatives from appearing |
| Set up dUTP+UNG enzyme anti-pollution system | prevent product contamination |
| Good repeatability | the precision between batches and batches are ≤5% |
| Good specificity | no cross-reaction in detection of multiple pathogens |
| Strong anti-interference ability | the detection will not be affected under the peak concentration of a variety of antiviral drugs |
Conventional fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument

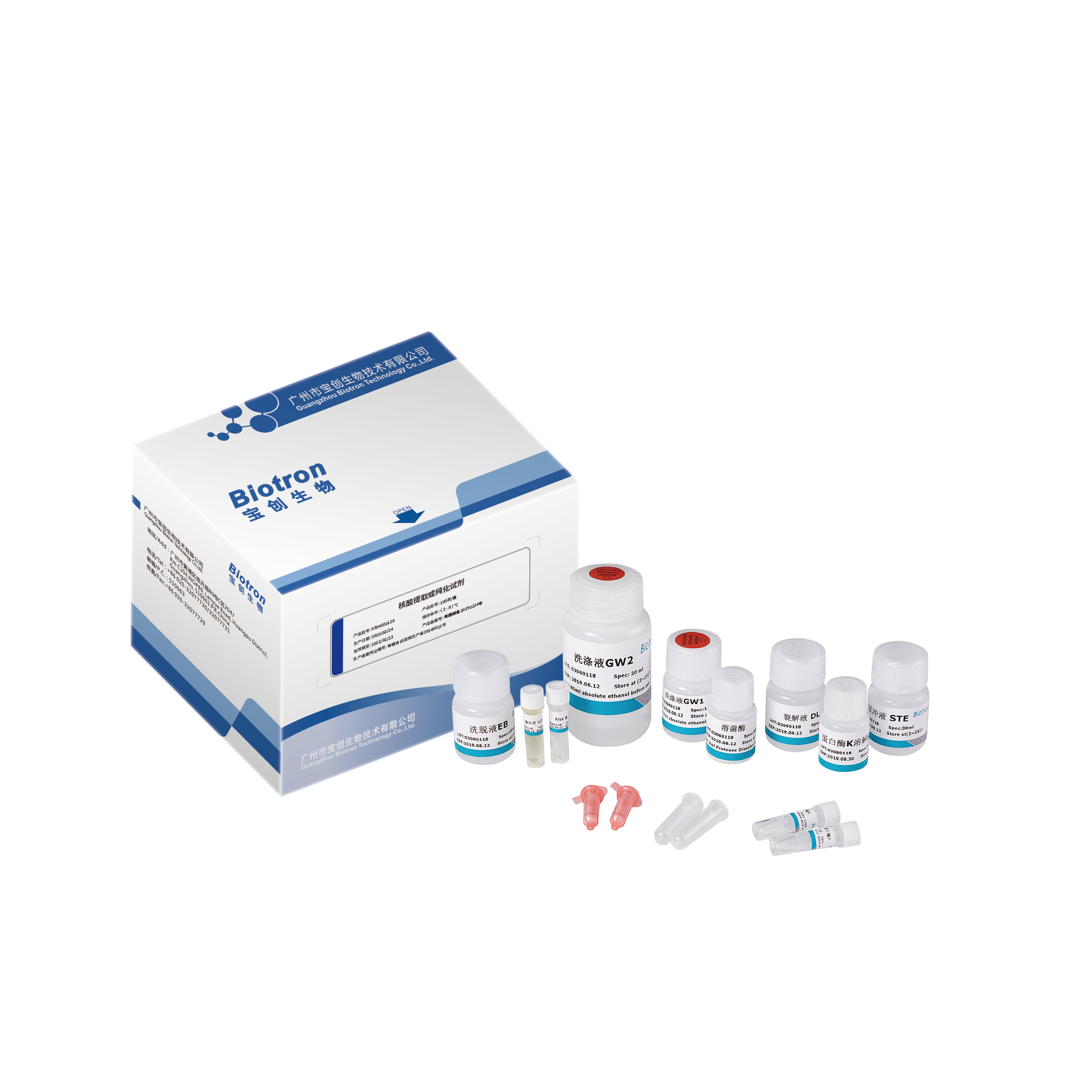
It is suitable for the nucleic acid extraction of whole blood, serum, plasma, tissue, bone marrow, paraffin-embedded tissue or section, urine, culture medium supernatant, cell-free body fluid, swab, tissue homogenate supernatant, cell culture medium, etc,enrichment and purification.
It is suitable for the nucleic acid extraction of whole blood, serum, plasma, tissue, bone marrow, paraffin-embedded tissue or section, urine, culture medium supernatant, cell-free body fluid, swab, tissue homogenate supernatant, cell culture medium, etc. Enrichment and purification.
The processed product is used for clinical in vitro testing.
| High-quality nucleic acid | Purified nucleic acid has the characteristics of high concentration, high purity, and good integrity |
| Wide application range | can handle various types of samples |
| Wide range of applications | to meet various downstream applications, such as PCR, quantitative PCR, restriction enzyme digestion, blot hybridization, etc. |




International Patent Technology
Easy to operate (Nucleic acid extraction, PCR amplification, Interpretation of results < 3 hours)
One 96-throughput thermal cycler can detect 94 samples in a single batch, more efficient
Fully automatic data analysis software, result interpretation is smarter and faster
High sensitivity, strong specificity
Cervical cancer is the fourth most frequently occurring cancer in women around the world, also affecting young women during their reproductive years, and estimated to kill 250,000 women annually. Since the development of the Papanicolaou (Pap) test, screening has been essential in identifying cervical cancer at a treatable stage. With the identification of the human papillomavirus (HPV) as the causative agent of essentially all cervical cancer cases, HPV molecular screening tests and HPV vaccines for primary prevention against the virus have been developed. HPV is however the most commonly acquired sexually transmitted virus, with around four out of five people (80%) contracting this infection at some point during their lifetime.
Currently available HPV tests are unable to discriminate HPV infections regressing spontaneously from those turning into cancer. Screening refusal is also an important problem in several European countries, mainly as a result of social, economic and/or racial/ethnic barriers, hindering cervical cancer prevention in these women. This, together with current failure to implement gender-neutral HPV vaccination with high coverage in the great majority of countries, have resulted in IARC’s projections showing that, unless innovative preventive measures are implemented promptly, the burden of cervical cancer is expected to increase to almost 460.000 deaths per year by 2040, an increase of nearly 50% over the estimated number of deaths in 2018.
Recommendation
WHO guideline for screening and treatment of cervical pre-cancer lesions for cervical cancer prevention, 2021.
HPV DNA testing as preferred method for cervical cancer screening
Clinical significance:
• Expanded testing for HPV types that cause cervical cancer
In addition to the 14 high-risk HPV types announced by WHO, the detection of intermediate-risk HPV types that may cause cancerous cells is added.
•Aids in the diagnosis of skin warts and genital related disorders
Includes testing for types 6 and 11 for HPV vaccine prophylaxis and testing for many other low-risk HPV types that cause skin warts.
•Prognosis of oropharyngeal carcinoma and establishment of individualized treatment plan
Patients with HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer have better treatment effect and prognosis than HPV-negative
patients, and de-escalation of treatment is an option.

International Patent Technology
Easy to operate (Nucleic acid extraction, PCR amplification, Interpretation of results < 3 hours)
One 96-throughput thermal cycler can detect 94 samples in a single batch, more efficient
Fully automatic data analysis software, result interpretation is smarter and faster
High sensitivity, strong specificity
Cervical cancer is the fourth most frequently occurring cancer in women around the world, also affecting young women during their reproductive years, and estimated to kill 250,000 women annually. Since the development of the Papanicolaou (Pap) test, screening has been essential in identifying cervical cancer at a treatable stage. With the identification of the human papillomavirus (HPV) as the causative agent of essentially all cervical cancer cases, HPV molecular screening tests and HPV vaccines for primary prevention against the virus have been developed. HPV is however the most commonly acquired sexually transmitted virus, with around four out of five people (80%) contracting this infection at some point during their lifetime.
Currently available HPV tests are unable to discriminate HPV infections regressing spontaneously from those turning into cancer. Screening refusal is also an important problem in several European countries, mainly as a result of social, economic and/or racial/ethnic barriers, hindering cervical cancer prevention in these women. This, together with current failure to implement gender-neutral HPV vaccination with high coverage in the great majority of countries, have resulted in IARC’s projections showing that, unless innovative preventive measures are implemented promptly, the burden of cervical cancer is expected to increase to almost 460.000 deaths per year by 2040, an increase of nearly 50% over the estimated number of deaths in 2018.
Recommendation
WHO guideline for screening and treatment of cervical pre-cancer lesions for cervical cancer prevention, 2021.
HPV DNA testing as preferred method for cervical cancer screening
Clinical significance:
• Expanded testing for HPV types that cause cervical cancer
In addition to the 14 high-risk HPV types announced by WHO, the detection of intermediate-risk HPV types that may cause cancerous cells is added.
•Aids in the diagnosis of skin warts and genital related disorders
Includes testing for types 6 and 11 for HPV vaccine prophylaxis and testing for many other low-risk HPV types that cause skin warts.
•Prognosis of oropharyngeal carcinoma and establishment of individualized treatment plan
Patients with HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer have better treatment effect and prognosis than HPV-negative
patients, and de-escalation of treatment is an option


Avoid missed tests for multiple infections/combinations multiple/combined infections effective information
Analysis software: realizing automatic interpretation
The minimum detection limit is not higher than 1000 copies/ml, with high accuracy and specificity.
Melting curve analysis method: detecting 12 pathogens respectively.
Fast reaction (5-10 minutes)
Respiratory tract infections are divided into upper respiratory tract infections and lower respiratory tract infections. Upper respiratory tract infections mainly manifest as fever, headache, tinnitus, cough, runny nose, nasal congestion, etc., and are dominated by viruses, accounting for 70% to 80%. Lower respiratory tract infections include pneumonia, tracheitis, bronchitis, capillary bronchitis, etc. Usually, lower respiratory tract infections are much more serious than upper respiratory tract infections, and the pathogens are more complex.
Acute upper respiratory infections occur in most people every year, 2 to 4 times per year in adults and in children at a higher rate of 6 to 8 times per year
Clinical significance:
Early Identification
Direct detection of pathogens, shorten pathogen reporting time, improve the pathogen detection rate, and improve detection of mixed infections
Precise treatment
Timely and accurate pathogenic results can promote the rational use of antibacterial drugs, facilitate infection control, and improve patient prognosis
Conserve medical resources
Optimize the treatment process, shorten hospital stays, and reduce treatment costs, resulting in clinical and economic benefits
Epidemic prevention and control
Screening and early warning of respiratory diseases, helping to normalize epidemic prevention and control, reducing the spread of respiratory diseases and infections in groups



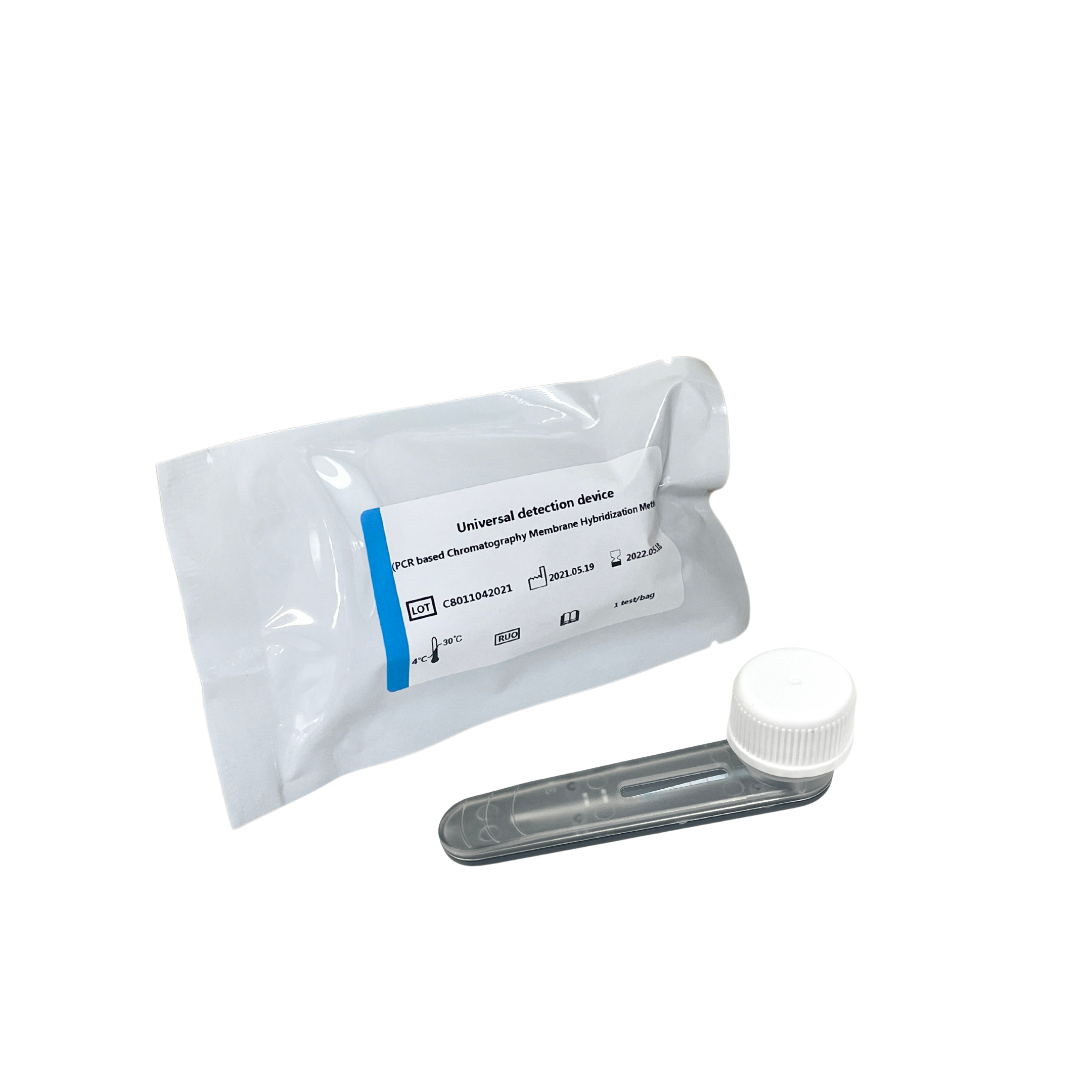
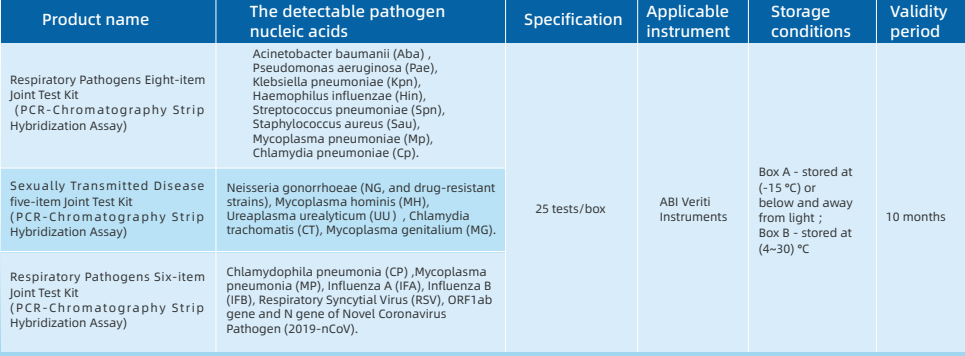
Five-term Respiratory Pathogens Test Kit
Seven-term Respiratory Pathogens Test Kit
Four-term Sexually Transmitted Diseases Pathogens Test Kit
PCR amplification reagent
The PCR amplification reaction uses the patented technology STH-PAS (Single Tag Hybridization-Printed Array Strip),
through a pair of 5'-end specially modified specific primers, with PCR reaction solution, hot-start Taq enzyme and other components for specificity PCR amplification.
Detection device
Followed by reconstitution and release of the PCR amplification product and blue latex microspheres in the detection device,
and the released amplification product hybridizes with the probe on the membrane strip and fixes it. Make a qualitative interpretation by the presence or absence of blue bands.
Advantage:
- Disposable anti-pollution detection device with the principle of physical isolation, does not need to open the cover to process PCR amplification products, which can effectively avoid false positives caused by aerosol diffusion of PCR amplification products.
- Adopts the dUTP-UNG enzyme anti-pollution system,eliminating the existing U-DNA pollutants in the reaction system or the environment.
- Equipped with internal standard system, negative control and positive control,participates in the parallel extraction and detection of sample nucleic acid.
Operate video:
Product name:


Five-term Respiratory Pathogens Test Kit
Seven-term Respiratory Pathogens Test Kit
Four-term Sexually Transmitted Diseases Pathogens Test Kit
PCR amplification reagent
The PCR amplification reaction uses the patented technology STH-PAS (Single Tag Hybridization-Printed Array Strip),
through a pair of 5'-end specially modified specific primers, with PCR reaction solution, hot-start Taq enzyme and other components for specificity PCR amplification.
Detection device
Followed by reconstitution and release of the PCR amplification product and blue latex microspheres in the detection device,
and the released amplification product hybridizes with the probe on the membrane strip and fixes it. Make a qualitative interpretation by the presence or absence of blue bands.
Advantage:
- Disposable anti-pollution detection device with the principle of physical isolation, does not need to open the cover to process PCR amplification products, which can effectively avoid false positives caused by aerosol diffusion of PCR amplification products.
- Adopts the dUTP-UNG enzyme anti-pollution system,eliminating the existing U-DNA pollutants in the reaction system or the environment.
- Equipped with internal standard system, negative control and positive control,participates in the parallel extraction and detection of sample nucleic acid.
Operate video:
Product name:



Five-term Respiratory Pathogens Test Kit
Seven-term Respiratory Pathogens Test Kit
Four-term Sexually Transmitted Diseases Pathogens Test Kit
PCR amplification reagent
The PCR amplification reaction uses the patented technology STH-PAS (Single Tag Hybridization-Printed Array Strip),
through a pair of 5'-end specially modified specific primers, with PCR reaction solution, hot-start Taq enzyme and other components for specificity PCR amplification.
Detection device
Followed by reconstitution and release of the PCR amplification product and blue latex microspheres in the detection device,
and the released amplification product hybridizes with the probe on the membrane strip and fixes it. Make a qualitative interpretation by the presence or absence of blue bands.
Advantage:
- Disposable anti-pollution detection device with the principle of physical isolation, does not need to open the cover to process PCR amplification products, which can effectively avoid false positives caused by aerosol diffusion of PCR amplification products.
- Adopts the dUTP-UNG enzyme anti-pollution system,eliminating the existing U-DNA pollutants in the reaction system or the environment.
- Equipped with internal standard system, negative control and positive control,participates in the parallel extraction and detection of sample nucleic acid.
Operate video:
Product name:




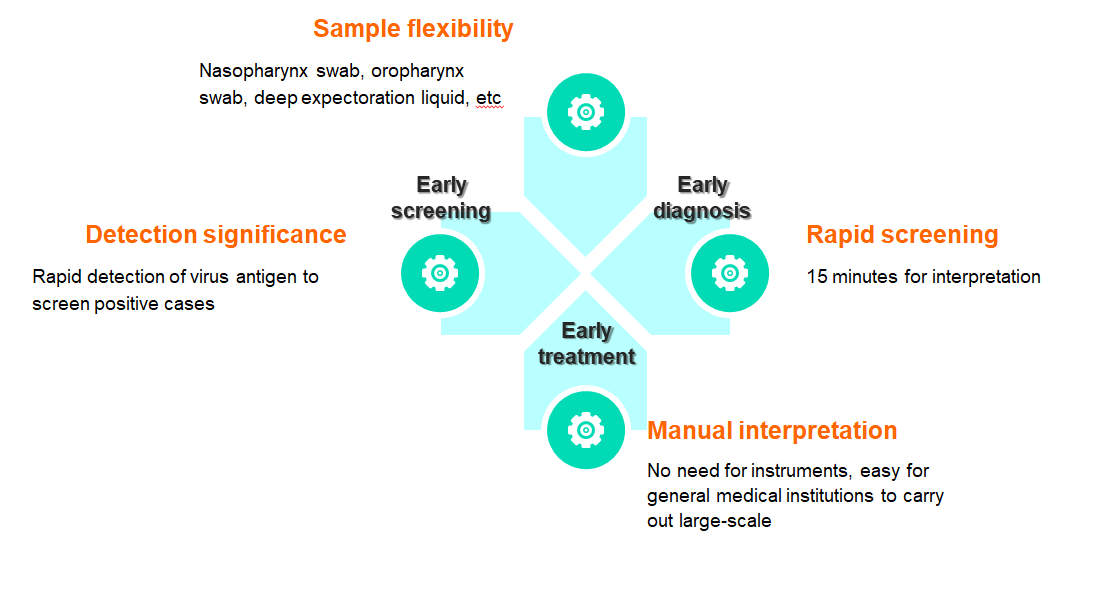
Flexible samples: nasopharyngeal swabs, oropharyngeal swabs, deep sputum, etc
Quick screening: results can be interpreted in 15 minutes
Manual interpretation: no equipment is needed, easy for general medical institutions to develop
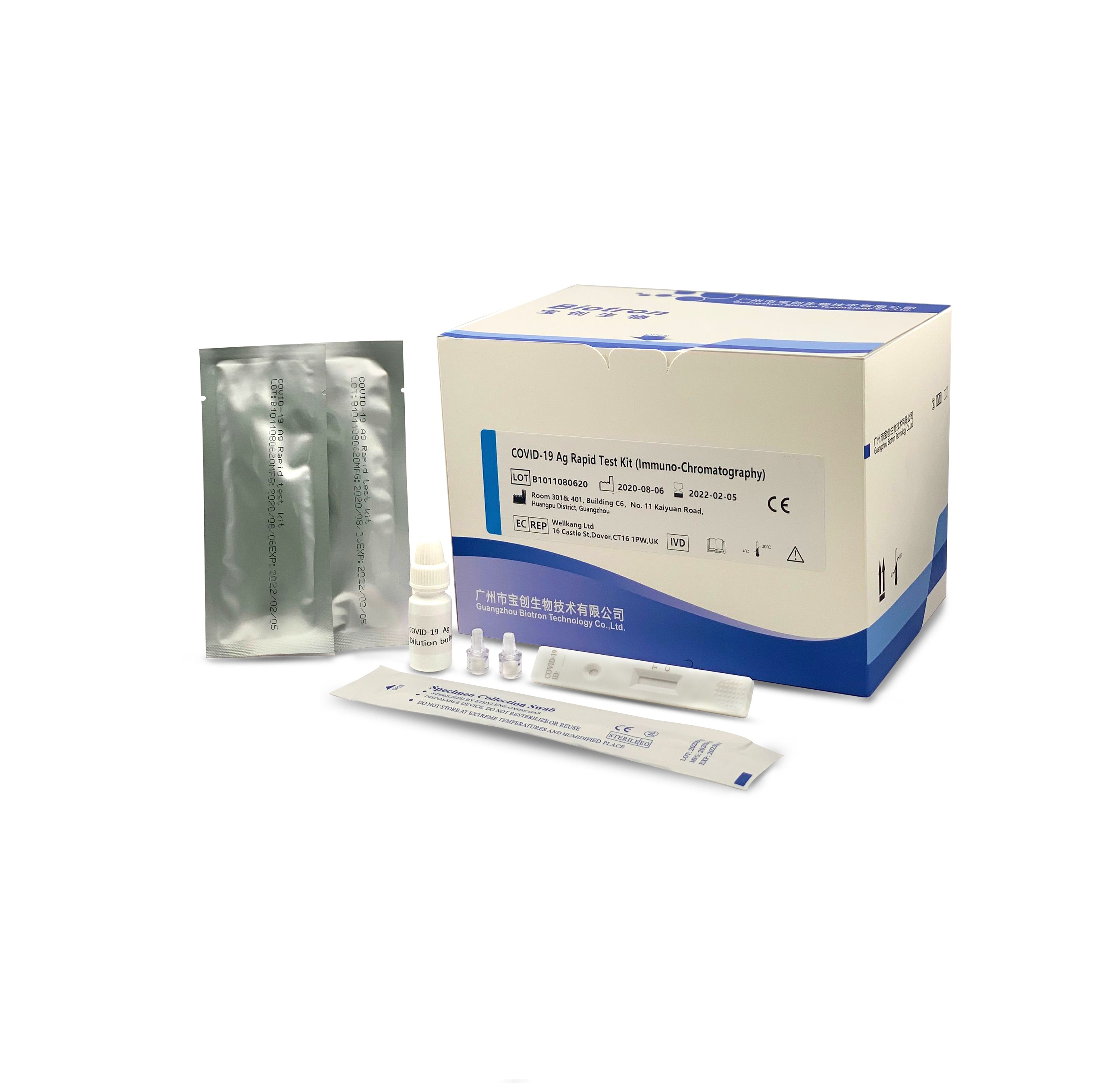
The reagent is used for clinical in vitro qualitative detection of novel coronavirus antigens in human throat swabs and other in vitro samples. This kit uses the principle of immuno-chromatography technology to detect the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) antigen in human throat swab samples using the double antibody sandwich method.
Product advantage
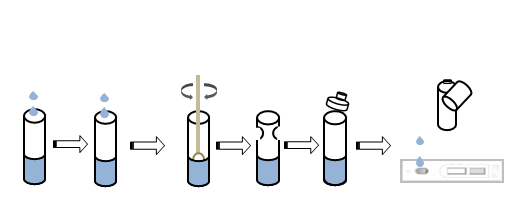
TEST PROCEDURE
| Sample type | nasopharyngeal swab, oropharyngeal swab, deep sputum |
| Report time | 15min |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 50 tests/box |


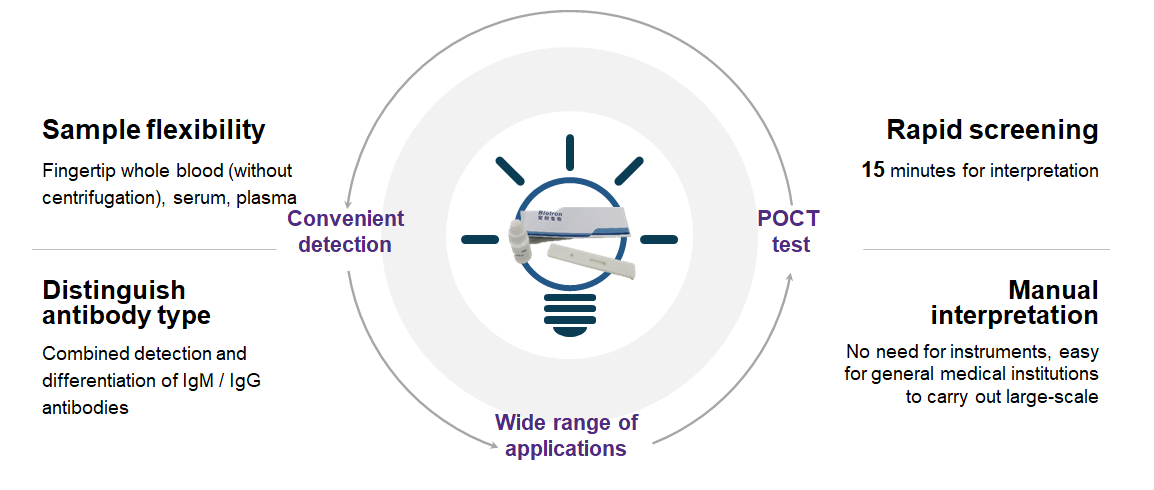
Flexible samples: fingertip whole blood (no need for centrifugation), serum, plasma
Quick screening: results can be interpreted in 15 minutes
Differentiating types: combined detection and distinguishing IgM/IgG antibodies
Manual interpretation: no equipment is needed, easy for general medical institutions to carry out a wide range
The reagent is used for the clinical in vitro qualitative detection of new coronavirus (2019-nCoV) antibodies in human serum, plasma or whole blood.
It is only used as a supplementary test indicator for suspected cases with a negative nucleic acid test of the new coronavirus or used in conjunction with nucleic acid testing in the diagnosis of suspected cases.
It cannot be used as a basis for the diagnosis and exclusion of pneumonia caused by new coronavirus infection, and is not suitable for screening of the general population. Only for medical institutions.
Product advantage
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood,fingertip blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 50 tests/box |

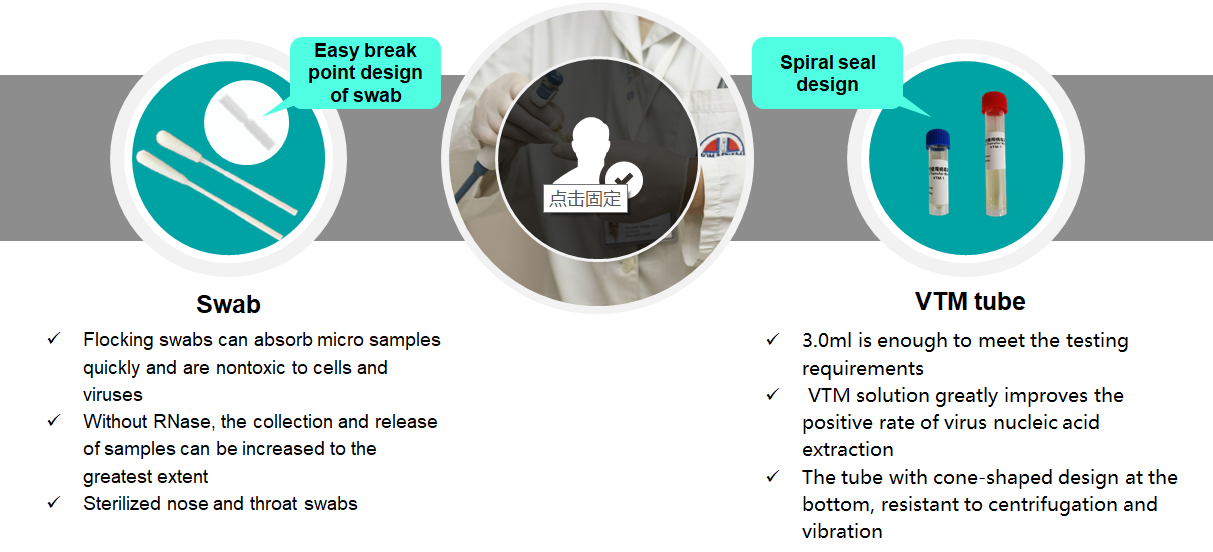
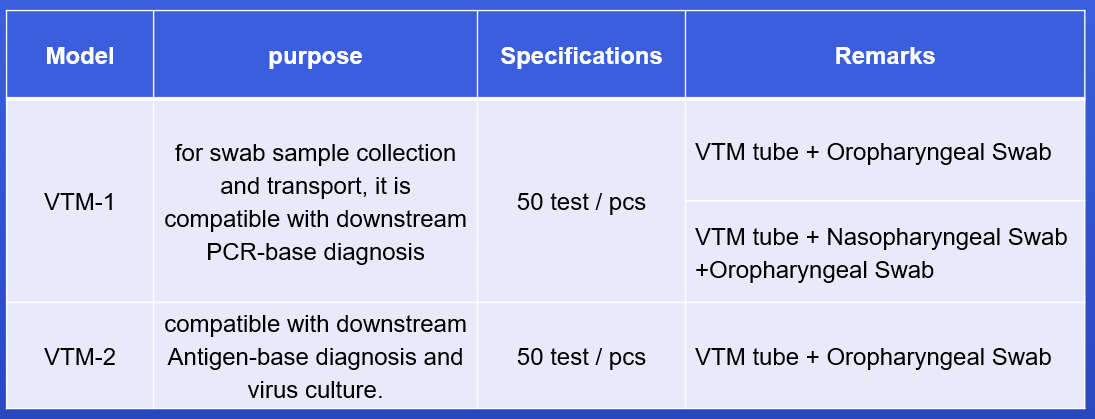
VTM tube with different types of swabs, easy to use
After sampling, it can be used for subsequent PCR detection or virus culture
Multiple configurations for different needs
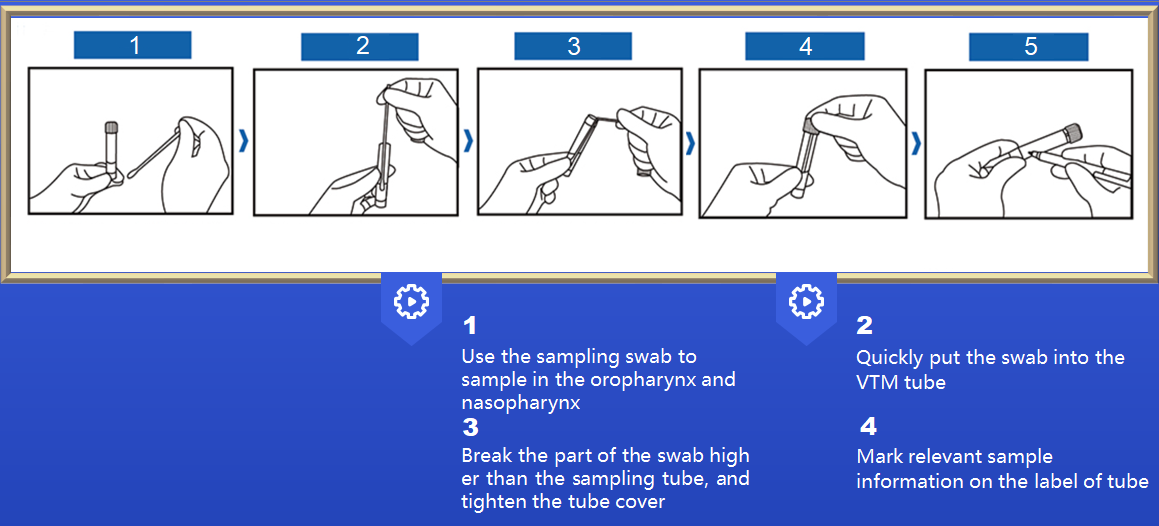
Viral Transport Medium (VTM) is ideal for diagnosis of viral infection. Ocular, respiratory and tissue swabs can be submitted in this medium. Fluid samples such as tracheal wash specimens or peritoneal fluid should be submitted as is, in sterile vials which prevent desiccation. Cotton, plastic, wood-handled, and Dacron and other synthetic swabs are all acceptable.
Product advantage
Instruction manual

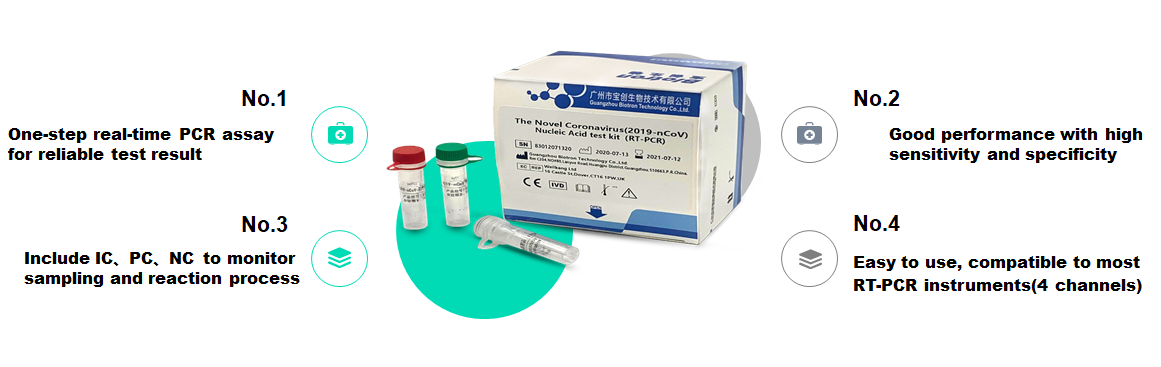
Reliable one-step real-time PCR detection results
High sensitivity and good specificity
Including IC, PC, NC to monitor the sampling and reaction process
Easy to use, compatible with most RT-PCR instruments (4 channels)
The 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), is a contagious virus that causes respiratory infection and has shown evidence of human-to-human transmission, first identified by authorities, as the cause of coronavirus outbreak all over the world. Genomic sequencing has shown that it is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA coronavirus. Rapid and accurate screening methods are highly desirable so that the correct treatment can be provided and to prevent further spread of such contagious infections.
The new coronavirus (2019 nCoV) nucleic acid detection kit is a single-closed test tube detection method for detecting coronavirus based on in vitro real-time PCR.
Product advantage
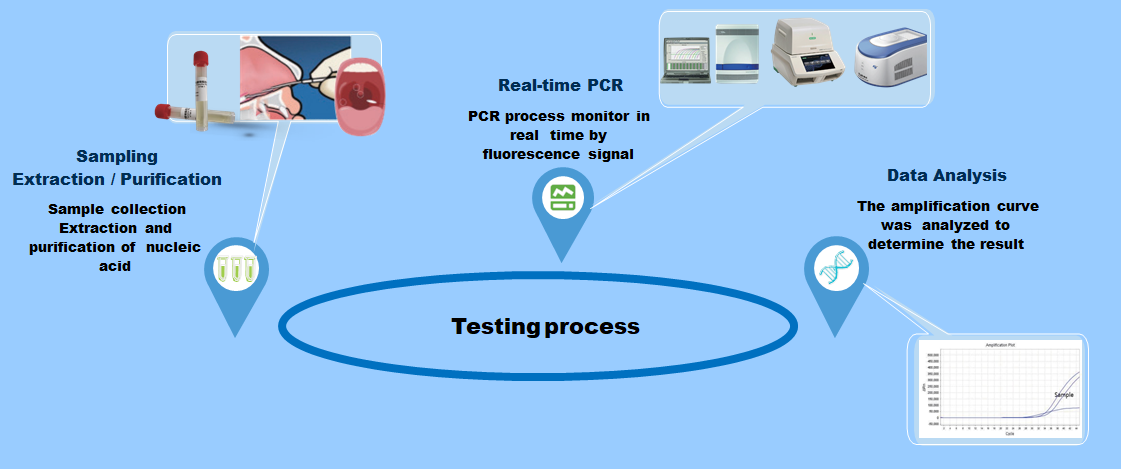
Test procedure
Performance parameter
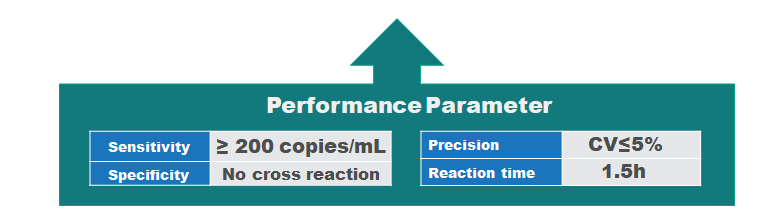
| Sample type | nasopharyngeal swab, oropharyngeal swab, deep sputum |
| Report time | 15h |
| Storage | -15°C |
| Validity period | 12 months |
| Specifications | 48 tests/box |



H-FABP Rapid Test (Fluorescence immunochromatography)


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood;
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and it incurs huge healthcare expenditures [1-4]. In the United States alone, 683,000 discharge occurrences resulting from ACS were reported in 2009 [5,6]. Remarkably, 1,190,000 secondary discharges were associated with ACS, of which 829,000 were attributed to myocardial infarction (MI) alone [5,6]. ACS is caused by the sudden obstruction of a coronary artery. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of ACS continues to be a diagnostic challenge in medicine, The highest risk of fatality occurs within the initial hours of onset of AMI. Thus, early diagnosis of cardiac ischemia is critical for the effective management of patients with AMI. Improper diagnosis of patients with chest pain often leads to inappropriate admission of patients without AMI and vice versa. In addition to clinical history, physical examination, accurate electrocardiogram findings and assessment of cardiac biomarkers have an important role in the early diagnosis of acute ischemia.
A marker of Myocardial Injury:
H-FABP: It is a small-molecule soluble protein that is abundant in the cytoplasm of myocardium, but when myocardial cells are damaged, it can be quickly released into the blood, leading to a sharp increase in the level of H-FABP in the blood high.H-FABP can be used as a predictive biomarker of mortality following acute coronary syndrome (ACS).

Clinical significance:
Detection for the early diagnosis and risk stratification of acute myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction area estimation Differential diagnosis of chest pain Prognostic evaluation of ACS
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | H-FABP≤7ng/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

cTnl/CK-MB/Myo Rapid Test Kit


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and it incurs huge healthcare expenditures [1-4]. In the United States alone, 683,000 discharge occurrences resulting from ACS were reported in 2009 [5,6]. Remarkably, 1,190,000 secondary discharges were associated with ACS, of which 829,000 were attributed to myocardial infarction (MI) alone [5,6]. ACS is caused by the sudden obstruction of a coronary artery. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of ACS continues to be a diagnostic challenge in medicine, The highest risk of fatality occurs within the initial hours of onset of AMI. Thus, early diagnosis of cardiac ischemia is critical for the effective management of patients with AMI. Improper diagnosis of patients with chest pain often leads to inappropriate admission of patients without AMI and vice versa. In addition to clinical history, physical examination, accurate electrocardiogram findings and assessment of cardiac biomarkers have an important role in the early diagnosis of acute ischemia.
Myocardial Injury Marker:
H-FABP: It is a small-molecule soluble protein that is abundant in the cytoplasm of myocardium, but when myocardial cells are damaged, it can be quickly released into the blood, leading to a sharp increase in the level of H-FABP in the blood high.H-FABP can be used as a predictive biomarker of mortality following acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
CTnI: It is a contractile protein that exists only in the myocardium. It is one of the three subunits of troponin complex (I, T, C), and combines with tropomyosin in the filaments of myofibrils to form actin.
Myo: Mainly present in the myocardium and skeletal muscle. When skeletal muscle and myocardium are damaged (acute myocardial infarction), excessive exercise and muscle diseases, myoglobin is released into the blood.The levels of MYO can therefore not be used as a single diagnostic marker, but in conjunction with the troponins or CK-MB. Thus, serum levels of MYO can be used to rule out, rather than diagnose, myocardial infarction (46).
CK-MB: a form of creatine kinase isoenzyme, which mainly exists in the myocardium. It is one of the important markers of myocardial injury and can effectively diagnose acute myocardial infarction.

Joint detection

The combined detection of the three items of myocardial infarction helps distinguish AMI patients in a timely and accurate manner, minimizes the damage, avoids missed diagnosis and misdiagnosis, and can win more precious time for timely rescue of patients with myocardial infarction.
Multi-index combined detection can improve the detection rate and accuracy of myocardial injury, reduce the missed diagnosis rate, and reduce doctor-patient disputes.
Clinical significance:
Combined detection for early diagnosis and risk stratification of acute myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction area estimation differential diagnosis of chest pain Prognostic evaluation of ACS
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | cTnI≤0.3ng/ml,Myo≤58ng/ml,CK-MB≤5ng/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |

NT-proBNP Rapid Test Kit (Fluorescence immunochromatography)


Applicable to various sample types of serum, plasma and whole blood
Rapid detection of single reagent (15 minutes)
Convenient storage and transportation at room temperature
Heart failure (HF) biomarkers have dramatically impacted the way HF patients are evaluated and managed. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP) are the gold standard biomarkers in determining the diagnosis and prognosis of HF, and studies on natriuretic peptide-guided HF management look promising.
NT-proBNP: A gold standard for Heart Failure
International guidelines recommend the use of B-type natriuretic peptide testing in the diagnostic workup of Heart Failure (HF) in both acute and non-acute patient presentation(2).
In the emergency department (ED), NT-proBNP is particularly useful for the triage of patients with acute dyspnea and suspected acute HF. It is highly sensitive and specific for exclusion (single rule-out cut-off value of 300 pg/mL) or confirmation of acute HF (age-adjusted rule-in cut-off values) (3).

*The area between the rule-out (<300pg/mL) and the rule-in (age-ajusted) cut-off values is designated as the "gray zone".
NT-proBNP in the evaluation and triage of ED patients with acute dyspnea (4)
In primary care, NT-proBNP is particularly useful to guide referral of symptomatic chronic HF to specialist care because it excludes suspected left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Compared with NT-proBNP values in patients with acute HF, lower values are expected in ambulatory chronic HF patients. International guidelines recommend a single low cut-off of 125pg/mL to rule out HF for patients presenting with non-acute symptoms. However peer-reviewed literature supports the use of age-dependent cut-offs to adjust for loss of specificity in such settings(5).

NT-proBNP in the primary care setting
Clinical significance:
Early elimination/diagnosis of heart failure, identification of causes of acute and chronic dyspnea Risk classification of patients with heart failure, prediction of adverse outcomes Efficacy monitoring, treatment guidance and prognosis evaluation for patients with heart failure
Applicable departments:
Cardiology, chest pain center, stroke center, emergency department, ICU, cardiac surgery, neurology, respiratory, etc.
References:
1. Moe G.W, Howlett J, Januzzi JL, et al. Primary results of the Canadian prospective randomized multicenter IMPROVE-CHF study. Circulation 2007;115: 3103-3110.
2. McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, et al.; ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1787-847
3. Januzzi JL, van Kimmenade R, et al. the International Collaborative of NT-proBNP Study. Eur Heart J. 2006 ;27:330-7.
4. Januzzi JL, Chen-Tournoux AA, Moe G. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101 (Suppl.):29A-38A.
5. Hildebrandt P, Collinson PO, et al. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:1881-9.
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Report time | 15min |
| Reference range | <75 years old, NT-proBNP≤300 pg/ml, ≥75 years old, NT-proBNP≤450 pg/ml |
| Storage | 4-30℃, sealed and kept away from light and dry |
| Validity period | 18 months |
| Specifications | 25 tests/box, 50 tests/box |
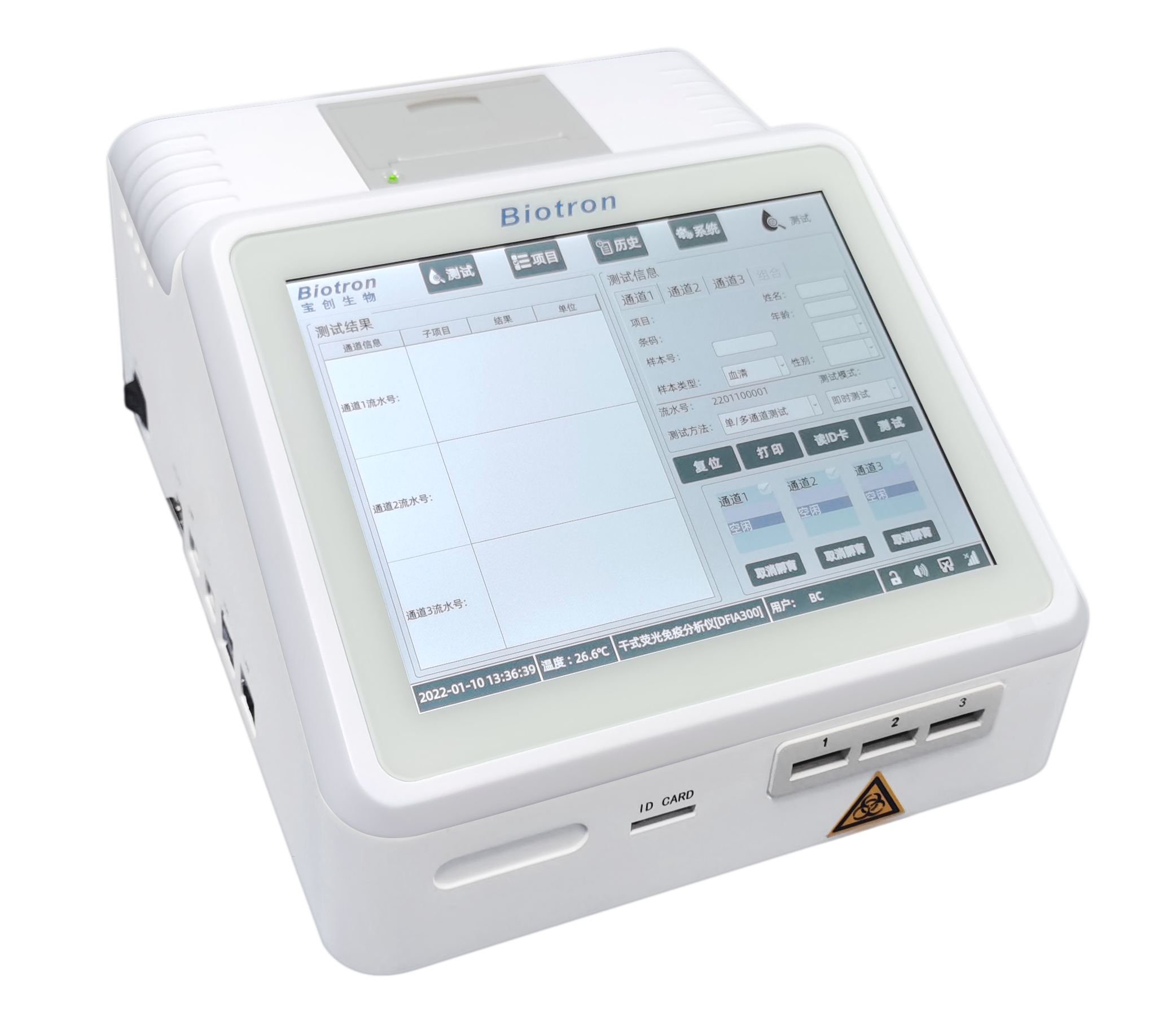

Dry immunofluorescence analyzer(DFIA300)


- Suitable for a wide range of sample types
- Three-channel instrument with the multi-sample batch testing capability
- Automated rapid quantification with single-sample reagent strips
Cooperate with special single reagent strips to realize the quantitative detection of a series of immunoassay items.
Supports single or multiple biomarkers for simultaneous detection and quantitative detection of a series of immunoassays
Product Model:DFIA300
Detection channel: 3 channels
Detection principle: dry fluorescence immunoassay
Sample type and blood volume requirements: serum, plasma, whole blood; ≤100µl
Display: 8-inch touch screen
Result transmission: support LIS transmission results

Dry immunofluorescence analyzer(DFIA200)


- Rotating 12-channel instrument with multi-sample batch detection capability
- Applicable to a variety of sample types
- Easy to operate, with a single reagent strip to automatically complete rapid quantitative detection
Cooperate with special single reagent strips to realize the quantitative detection of a series of immunoassay items.
| Product model | DFIA200 |
| Detection channel | 12-channel |
| Detection principle | dry fluorescence immunoassay |
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Blood volume requirements | ≤100µl |
| Detection speed | ≤ 15 minutes |
| Display | 8-inch color screen |
| Result transmission | support LIS transmission result |
| Detection method | support one card one item, one card multiple data processing |

Dry immunofluorescence analyzer(DFIA100)


- Single-channel instrument, light and compact
- Applicable to a variety of sample types
- Easy to operate, with a single reagent strip to automatically complete rapid quantitative detection
Cooperate with special single reagent strips to realize the quantitative detection of a series of immunoassay items.
| Product model | DFIA100 |
| Detection channel | single channel |
| Detection principle | dry fluorescence immunoassay |
| Sample type | serum, plasma, whole blood |
| Blood volume requirements | ≤100µl |
| Detection speed | ≤ 15 minutes |
| Display | 7-inch touch screen |
| Result transmission | support LIS transmission result |
| Detection method | support one card one item, one card multiple data processing |

